Overview
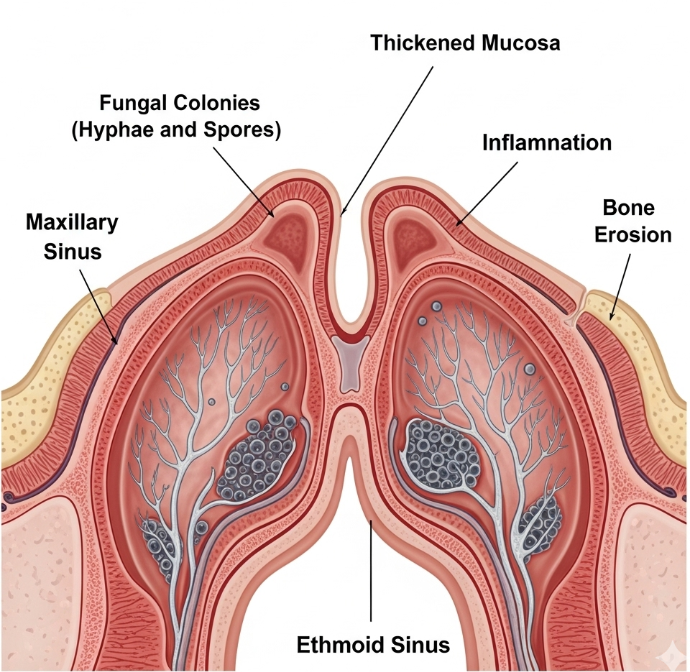
Fungal sinusitis is a condition where fungal organisms infect the sinuses, leading to inflammation and nasal obstruction. In Korea, it is more commonly seen in patients with chronic sinus issues, weakened immunity, or allergies. While many cases are mild, invasive fungal sinusitis can be severe and life-threatening, especially in immunocompromised individuals.
What is Fungal Sinusitis?
Fungal sinusitis occurs when fungi colonize or invade the paranasal sinuses, causing inflammation. There are two main types:
- Non-invasive: Fungal balls or allergic fungal sinusitis (AFS)
- Invasive: Tissue-invasive forms, more common in immunocompromised patients
It can affect any age group, but severity and complications increase in older adults or those with chronic illnesses.
Symptoms
- Nasal congestion and blockage
- Facial pain or pressure
- Post-nasal drip or thick nasal discharge
- Loss of smell (anosmia)
- Headache
- Fever and malaise in invasive cases
- Swelling around eyes or nose in severe infections
Causes
- Aspergillus species or other environmental fungi
- Allergic reactions to fungal spores (in AFS)
- Weakened immune system, such as in diabetes, chemotherapy, or HIV
- Previous sinus surgery or chronic sinusitis
Risk Factors
- Immunocompromised conditions
- Diabetes mellitus
- Chronic sinus infections or nasal polyps
- Exposure to moldy environments
- Allergic rhinitis or asthma
Complications
- Chronic sinusitis
- Invasive fungal infection affecting orbit or brain (rare but serious)
- Vision problems if the infection spreads to the eyes
- Bone destruction in severe cases
- Hospitalization and surgical intervention if untreated
Prevention
- Maintain good nasal hygiene
- Avoid exposure to moldy or dusty environments
- Manage allergies and chronic sinusitis effectively
- Control blood sugar levels in diabetic patients
- Prompt treatment of sinus infections to prevent fungal colonization
Treatment Options in Korea
Diagnosis
- Nasal endoscopy to visualize fungal growth
- CT or MRI scans to assess sinus involvement
- Fungal cultures and histopathology for species identification
- Allergy testing in cases of allergic fungal sinusitis
Medical Treatments
- Antifungal medications (oral or intravenous) for invasive cases
- Nasal corticosteroids to reduce inflammation
- Saline irrigation for non-invasive cases
Surgical Treatments
- Endoscopic sinus surgery to remove fungal debris and polyps
- Debridement of infected tissue in invasive forms
- Reconstruction or repair if sinus structure is damaged
Supportive Care & Follow-Up
- Regular ENT follow-up to monitor recurrence
- Allergy management for patients with AFS
- Long-term monitoring for high-risk patients