Overview
Fungal infections are caused by fungi invading the skin, nails, hair, or internal organs. In Korea, these infections are common due to humid summers, crowded living conditions, and frequent use of communal spaces like gyms and public baths. While many fungal infections are mild and treatable, systemic infections can occur in people with weakened immune systems, making timely treatment essential.
What is Fungal Infection?
A fungal infection, also known as mycosis, occurs when fungi grow uncontrollably in or on the body. Common types include:
- Superficial infections: affecting skin, nails, and hair
- Subcutaneous infections: affecting deeper skin layers
- Systemic infections: affecting internal organs (rare but serious)
Fungal infections can affect people of all ages, but those with diabetes, immune disorders, or chronic illnesses are at higher risk.
Symptoms
- Red, itchy, or scaly skin
- Rash or circular patches (commonly known as ringworm)
- Thickened or discolored nails
- Hair loss in affected areas
- Blisters or pus-filled lesions in severe cases
- Fever or malaise for systemic infections
Causes
- Overgrowth of Candida species (yeast infections)
- Dermatophytes causing skin, nail, and hair infections
- Aspergillus and other molds causing lung or systemic infections
- Weakened immune system or chronic illnesses
- Poor hygiene or prolonged moisture exposure
Risk Factors
- Diabetes or other metabolic disorders
- Immunosuppressive therapy or conditions (e.g., chemotherapy, HIV)
- Use of communal showers, gyms, or pools
- Warm, humid climate exposure
- Prolonged antibiotic or steroid use
Complications
- Chronic or recurrent skin and nail infections
- Systemic infections in immunocompromised individuals
- Secondary bacterial infections from scratched skin
- Discomfort or pain affecting daily activities
- Rarely, organ damage from untreated systemic mycoses
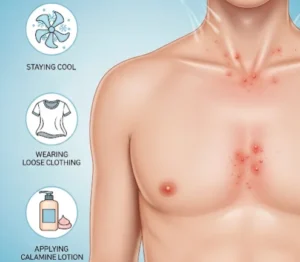
Prevention
- Maintain good personal hygiene
- Keep skin dry and clean, especially in folds and between toes
- Avoid sharing towels, shoes, or personal items
- Use antifungal powders or sprays in damp environments
- Promptly treat minor fungal infections to prevent spread
Treatment Options in Korea
Diagnosis
- Physical examination of affected areas
- Skin scrapings, nail clippings, or hair samples for microscopic analysis
- Culture tests to identify the fungal species
- Blood tests or imaging for suspected systemic infections
Medical Treatments
- Topical antifungal creams, gels, or ointments for mild skin infections
- Oral antifungal medications (e.g., fluconazole, itraconazole) for severe or nail infections
- Antifungal shampoos for scalp involvement
- Systemic therapy in hospitals for invasive infections
Supportive Care & Follow-Up
- Regular monitoring of chronic infections
- Lifestyle adjustments to prevent recurrence
- Patient education on proper hygiene and infection control