Overview
Frozen shoulder, also known as adhesive capsulitis, is a condition where the shoulder joint becomes stiff and painful, significantly reducing mobility. In Korea, it is a common musculoskeletal complaint, particularly among middle-aged adults and postoperative or diabetic patients. Timely diagnosis and treatment are important to restore function and reduce chronic pain.
What is Frozen Shoulder?
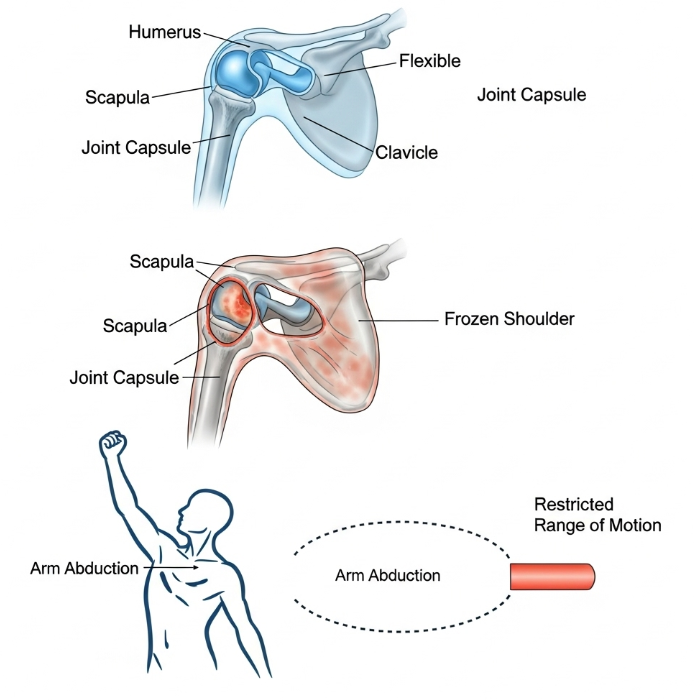
Frozen shoulder is characterized by inflammation and thickening of the shoulder joint capsule, leading to restricted movement and pain. It typically develops gradually and may persist for months to years. The condition can affect one or both shoulders, though usually one shoulder is affected at a time.
It commonly affects adults aged 40–60, with a higher prevalence in women and individuals with diabetes or thyroid disorders.
Symptoms
- Pain and stiffness in the shoulder
- Limited range of motion in all directions
- Difficulty with overhead activities
- Night pain interfering with sleep
- Gradual improvement followed by persistent mobility limitation if untreated
Causes
- Inflammation of the joint capsule for unknown reasons (primary frozen shoulder)
- Shoulder injury or surgery (secondary frozen shoulder)
- Prolonged immobilization after fracture or surgery
- Systemic conditions like diabetes, thyroid disorders, or cardiovascular disease
Risk Factors
- Diabetes mellitus (higher incidence)
- Age 40–60 years
- Women more than men
- History of shoulder injuries or surgeries
- Prolonged immobility due to other medical conditions
Complications
- Chronic shoulder pain and stiffness
- Difficulty performing daily activities
- Secondary muscle weakness around the shoulder
- Potential development of arthritis in severe, long-standing cases
Prevention
- Early physical therapy after shoulder injury or surgery
- Gentle range-of-motion exercises for shoulder joints
- Maintain good posture and ergonomics
- Control chronic conditions like diabetes
- Avoid prolonged immobilization of the shoulder
Treatment Options in Korea
Diagnosis
- Physical examination and evaluation of shoulder mobility
- X-rays to rule out fractures or arthritis
- MRI or ultrasound to assess soft tissue inflammation
Medical Treatments
- Pain relief with NSAIDs or corticosteroids
- Intra-articular steroid injections for severe inflammation
- Anti-inflammatory medications to reduce joint capsule swelling
Therapies and Rehabilitation
- Physiotherapy for range-of-motion and strength recovery
- Stretching exercises under professional guidance
- Heat therapy and massage to reduce stiffness
Surgical & Advanced Therapies
- Manipulation under anesthesia (MUA) for severe cases
- Arthroscopic capsular release to remove scar tissue
- Minimally invasive surgery in specialized hospitals for persistent cases