Overview
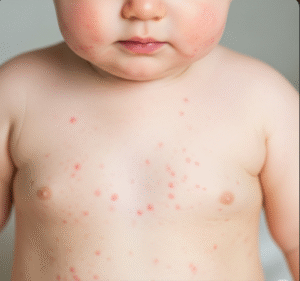
Food allergies are immune system reactions to certain foods that the body mistakenly identifies as harmful. Symptoms can range from mild itching or hives to severe anaphylaxis, which can be life-threatening. In Korea, awareness of food allergies has increased, and medical facilities provide diagnosis, treatment, and management plans for patients, including children and adults.
What are Food Allergies?
A food allergy occurs when the immune system reacts abnormally to specific proteins in foods, triggering the release of chemicals like histamine. Common allergens include peanuts, eggs, milk, shellfish, soy, and wheat. Reactions can be immediate (within minutes) or delayed (hours after ingestion).
Symptoms
- Hives or skin rash
- Swelling of lips, tongue, or face
- Itching or tingling in the mouth
- Gastrointestinal symptoms: nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain
- Respiratory symptoms: coughing, wheezing, nasal congestion
- Anaphylaxis: difficulty breathing, drop in blood pressure, dizziness
Causes
- Inherited genetic predisposition to allergies
- Early exposure to allergenic foods
- Immune system sensitivity to specific proteins
- Cross-reactivity with environmental allergens (e.g., pollen-food syndrome)
Risk Factors
- Family history of allergies or asthma
- Young children are more prone to developing food allergies
- Existing allergic conditions (eczema, asthma, rhinitis)
- Repeated exposure to allergenic foods at a young age
Complications
- Anaphylaxis requiring emergency treatment
- Nutritional deficiencies if major food groups are avoided without alternatives
- Chronic gastrointestinal problems in some patients
- Social and psychological impact due to dietary restrictions
Prevention
- Early introduction of allergenic foods in infants, as advised by pediatricians
- Breastfeeding when possible for the first six months
- Reading food labels carefully to avoid allergens
- Education for parents, caregivers, and schools on recognizing allergic reactions
- Carrying emergency medication, such as epinephrine auto-injectors, if prescribed
Treatment Options in Korea
Diagnosis:
- Detailed medical and dietary history
- Skin prick tests to identify specific allergens
- Blood tests for allergen-specific IgE antibodies
- Oral food challenges under medical supervision
Medical Treatments:
- Avoidance of allergenic foods is the primary strategy
- Antihistamines for mild allergic reactions
- Corticosteroids for severe inflammation
- Epinephrine auto-injectors for life-threatening anaphylaxis
Rehabilitation & Support:
- Dietary counseling to ensure nutritional adequacy
- Allergy education programs in schools and workplaces
- Emergency action plans for patients with severe allergies
- Regular follow-up to monitor tolerance or changes in allergy status