Overview
Folliculitis is a common skin condition in which hair follicles become inflamed, often due to bacterial, fungal, or viral infections. While generally mild, folliculitis can cause discomfort, itching, and sometimes scarring if untreated. In Korea, dermatology clinics provide modern diagnostic and treatment approaches, including topical therapies, antibiotics, laser treatment, and preventive skincare guidance.
What is Folliculitis?
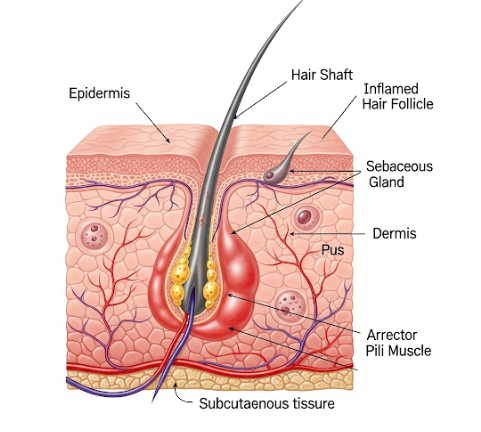
Folliculitis occurs when the hair follicles, the tiny openings from which hair grows, become infected or irritated. It can appear anywhere on the body, especially areas subjected to friction, shaving, or sweating. Folliculitis can be:
- Superficial: Affects the upper part of the hair follicle, usually mild.
- Deep: Involves the entire hair follicle, potentially causing painful nodules or abscesses.
Symptoms
- Small red or white pus-filled bumps around hair follicles
- Itching, tenderness, or pain in affected areas
- Redness and inflammation of the skin
- Crusting or oozing of lesions
- Swollen or painful lymph nodes in severe infections
Causes
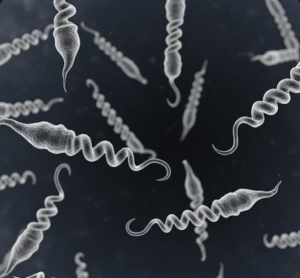
- Bacterial infections: Staphylococcus aureus is the most common cause
- Fungal infections: Yeast or dermatophyte infections
- Viral infections: Herpes simplex virus in rare cases
- Friction from tight clothing or shaving
- Excessive sweating or humid environments
- Blocked hair follicles due to oils, cosmetics, or skincare products
Risk Factors
- Shaving, waxing, or using hot tubs
- Obesity or diabetes
- Weakened immune system
- Prolonged antibiotic or steroid use
- Hot, humid climates
- Close contact with infected individuals
Complications
- Spread of infection to surrounding skin
- Boils or furuncles requiring drainage
- Scarring or pigmentation changes
- Recurring folliculitis in chronic cases
- Rare systemic infections in immunocompromised patients
Prevention
- Maintain good personal hygiene
- Avoid sharing towels, razors, or personal items
- Shave carefully or use alternatives to shaving
- Wear loose-fitting clothing to reduce friction
- Keep skin dry and clean, especially in humid conditions
- Treat underlying conditions like diabetes or immune disorders
Treatment Options in Korea
Diagnosis:
- Physical examination by a dermatologist
- Skin swabs or cultures to identify bacterial or fungal pathogens
- Biopsy in chronic or unusual cases
Medical Treatments:
- Topical antibiotics or antifungals for localized infections
- Oral antibiotics for more extensive bacterial folliculitis
- Antiviral medications if viral causes are suspected
- Anti-inflammatory creams to reduce itching and swelling
Surgical or Advanced Interventions:
- Incision and drainage of abscesses or boils
- Laser therapy in chronic or recurrent cases to reduce hair follicle inflammation
Rehabilitation & Support:
- Education on skincare and hygiene
- Avoiding triggers like harsh shaving or tight clothing
- Follow-up visits for persistent or recurrent cases
- Management of underlying risk factors (diabetes, immune suppression)