Overview
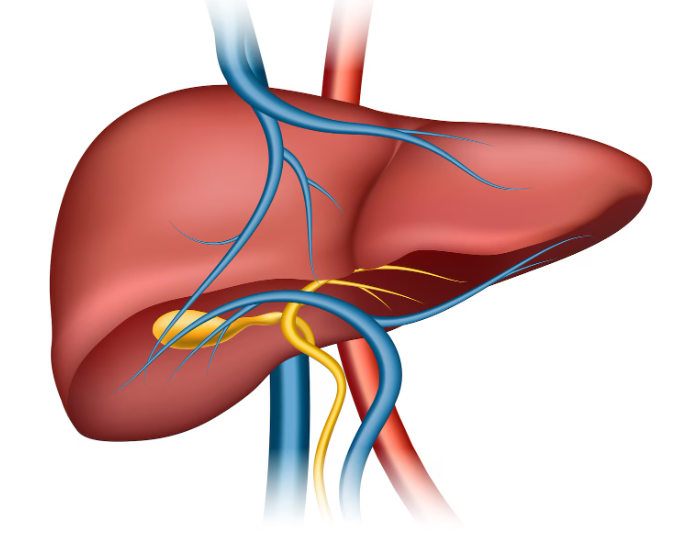
Fatty liver disease, also known as hepatic steatosis, is a condition where excess fat accumulates in liver cells. It is increasingly common in Korea due to dietary habits, obesity, and metabolic syndrome. Early detection and lifestyle modifications are key to preventing progression to non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), cirrhosis, or liver cancer.
What is Fatty Liver?
Fatty liver occurs when fat constitutes more than 5–10% of the liver’s weight. It can be alcoholic (caused by excessive alcohol intake) or non-alcoholic (NAFLD), often associated with obesity, diabetes, and high cholesterol. While mild cases may be asymptomatic, severe forms can cause liver inflammation and scarring.
Symptoms
- Often asymptomatic in early stages
- Fatigue or general malaise
- Mild abdominal discomfort in the upper right abdomen
- Unexplained weight loss in advanced cases
- Elevated liver enzymes detected on blood tests
Causes
- Obesity and metabolic syndrome
- High-fat or high-sugar diet
- Type 2 diabetes or insulin resistance
- Excessive alcohol consumption (for alcoholic fatty liver)
- Certain medications (e.g., corticosteroids, tamoxifen)
Risk Factors
- Obesity and overweight
- High cholesterol and triglycerides
- Type 2 diabetes or prediabetes
- Sedentary lifestyle
- Age over 40
- Genetic predisposition
Complications
- Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH)
- Liver fibrosis and cirrhosis
- Liver cancer (hepatocellular carcinoma)
- Increased risk of cardiovascular disease
- Potential liver failure in severe, untreated cases
Prevention
- Maintain a healthy weight and balanced diet
- Regular physical activity (at least 150 minutes per week)
- Limit alcohol consumption
- Control blood sugar, cholesterol, and triglyceride levels
- Routine liver function tests for high-risk individuals
Treatment Options in Korea
Diagnosis
- Blood tests to check liver enzymes (ALT, AST)
- Ultrasound, CT, or MRI to assess fat accumulation
- FibroScan to measure liver stiffness and detect fibrosis
- Liver biopsy in uncertain or advanced cases
Medical Treatments
- Lifestyle modification: diet, exercise, and weight loss
- Medications to manage underlying conditions: diabetes, high cholesterol
- Antioxidants or hepatoprotective agents in selected cases
Surgical or Advanced Therapies
- Bariatric surgery for obese patients with NAFLD/NASH
- Liver transplantation in end-stage liver disease
- Participation in clinical trials for novel therapies
Rehabilitation and Support
- Nutritional counseling and structured exercise programs
- Regular monitoring of liver function and metabolic health
- Support groups for lifestyle changes and chronic disease management