Overview
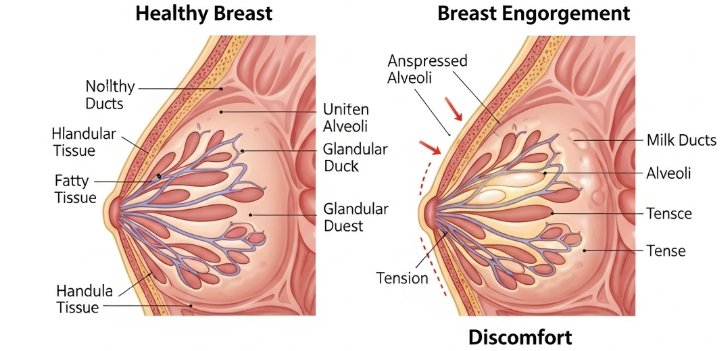
Engorgement refers to the painful swelling and fullness of the breasts, usually due to an increase in milk volume, blood flow, and lymphatic fluid. It commonly occurs in breastfeeding women during the first few days postpartum or when milk supply exceeds demand. South Korea provides both medical and lactation support to relieve symptoms and prevent complications.
What is Engorgement?
Engorgement happens when the breasts become overly full, firm, and sometimes tender, often making breastfeeding uncomfortable. It can interfere with proper latch, cause nipple pain, and in severe cases, lead to blocked ducts or mastitis.
Symptoms
- Swollen, hard, or warm breasts
- Tenderness or pain in the breasts
- Skin that appears shiny or stretched
- Flattened nipples, making latching difficult
- Mild fever in some cases
- Discomfort during breastfeeding
Causes
Engorgement can occur due to:
- Increased milk production after birth
- Irregular breastfeeding or skipped feeds
- Delayed initiation of breastfeeding
- Sudden weaning or stopping nursing
- Poor latch or ineffective milk removal
Risk Factors
- First-time mothers
- Overproduction of breast milk
- Breastfeeding difficulties in newborns (e.g., weak suck)
- Using breast pumps excessively or inconsistently
- Sudden changes in feeding schedule
Complications
- Blocked milk ducts
- Mastitis (breast infection)
- Painful breastfeeding leading to early weaning
- Skin cracking or nipple injury
- Anxiety or stress due to breastfeeding difficulties
Prevention
- Breastfeed frequently and on demand (8–12 times/day in newborns)
- Ensure proper latch and positioning
- Avoid long gaps between feeds
- Express milk gently if breasts feel overfull
- Wear supportive yet non-restrictive bras
- Stay hydrated and maintain good nutrition
Treatment Options in Korea
South Korea offers comprehensive lactation care and medical support for engorgement:
- Lactation Support
- Guidance from certified lactation consultants
- Techniques to improve latch and milk removal
- Education on breast massage and hand expression
- Medication (if needed)
- Pain relief with acetaminophen or ibuprofen
- Anti-inflammatory creams for localized discomfort
- Mechanical Assistance
- Breast pumps for controlled milk expression
- Cold compresses to reduce swelling and pain
- Warm compresses before feeding to promote letdown
- Hospital & Outpatient Care
- Major hospitals like Seoul National University Hospital and Samsung Medical Center offer lactation clinics with multidisciplinary teams including obstetricians, pediatricians, and nurses for postpartum support.
- Follow-Up & Education
- Monitoring for signs of mastitis or infection
- Guidance on gradual weaning if necessary
- Emotional and psychological support for breastfeeding mothers