Overview
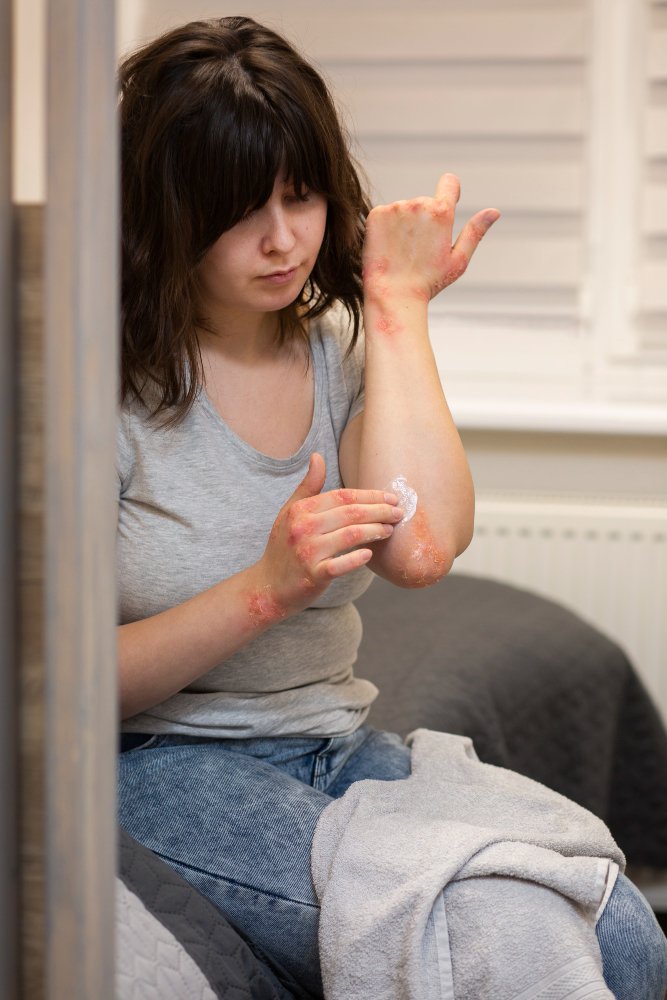
Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a chronic inflammatory skin condition that causes red, itchy, and irritated skin. It often develops in childhood but can affect individuals at any age. Eczema is not contagious, but it can significantly impact quality of life due to persistent itching, skin damage, and emotional distress. In South Korea, patients have access to advanced dermatology care and modern treatment options to manage and alleviate eczema symptoms effectively.
What is Eczema?
Eczema is a condition characterized by inflammation of the skin due to an overactive immune response. The skin barrier becomes weak, making it more susceptible to irritants, allergens, and infections. Eczema can appear in localized areas such as the hands, face, or elbows, or it may cover larger areas of the body.
Symptoms
Symptoms of eczema can vary based on age and severity:
- Red, inflamed skin
- Itching, often severe and persistent
- Dry, scaly, or cracked skin
- Blisters that may ooze or crust
- Thickened or rough skin in chronic cases
- Darkened patches of skin (hyperpigmentation) due to repeated scratching
Causes
The exact cause of eczema is multifactorial and includes:
- Genetic predisposition (family history of eczema, asthma, or allergies)
- Overactive immune response to environmental triggers
- Skin barrier dysfunction
- Allergens such as pollen, dust mites, and pet dander
- Irritants like soaps, detergents, and harsh chemicals
- Stress and hormonal changes
Risk Factors
- Personal or family history of atopic conditions
- Exposure to environmental irritants or allergens
- Living in urban areas with pollution
- Dry or cold climates that can aggravate skin dryness
- Early childhood infections or immune system imbalances
Complications
If left untreated, eczema can lead to:
- Skin infections caused by bacteria, viruses, or fungi
- Sleep disturbances due to intense itching
- Emotional and psychological stress, anxiety, or depression
- Thickened or permanently scarred skin from chronic scratching
Prevention
While eczema cannot always be prevented, flare-ups can be minimized by:
- Moisturizing the skin regularly to maintain the skin barrier
- Avoiding known triggers or allergens
- Using mild, fragrance-free soaps and detergents
- Wearing soft, breathable clothing
- Managing stress levels and maintaining healthy sleep habits
Treatment Options in Korea
South Korea offers comprehensive dermatology services, including modern medical treatments, therapy, and follow-up care for eczema:
- Diagnosis
- Physical examination of affected skin areas
- Allergy testing (skin prick or blood tests) to identify triggers
- Assessment of medical and family history
- Medication
- Topical corticosteroids for reducing inflammation
- Topical calcineurin inhibitors for sensitive areas
- Antihistamines to relieve itching
- Moisturizers and barrier repair creams
- Advanced Treatments
- Phototherapy (UV light therapy) for moderate to severe cases
- Biologic medications such as Dupilumab for severe, treatment-resistant eczema
- Lifestyle & Supportive Care
- Guidance on trigger avoidance and skin care routines
- Education for patients and caregivers on managing flare-ups
- Psychological support for coping with chronic symptoms
- Hospitals & Clinics
Major dermatology centers and hospitals in Korea include:- Seoul National University Hospital Dermatology Department
- Samsung Medical Center
- Asan Medical Center
- CHA Bundang Medical Center