Overview
Dystonia is a neurological movement disorder characterized by involuntary, sustained muscle contractions that cause twisting, repetitive movements, or abnormal postures. It can affect one part of the body (focal dystonia), multiple regions (segmental dystonia), or the entire body (generalized dystonia).
In Korea, the diagnosis and treatment of dystonia are advancing rapidly, thanks to specialized neurology and movement disorder centers. With access to state-of-the-art brain imaging, genetic testing, and surgical interventions like Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS), Korea is recognized as a hub for advanced movement disorder management in Asia.
What is Dystonia?
Dystonia is a disorder of the basal ganglia, the brain region responsible for controlling movement. Patients may experience involuntary contractions that interfere with daily activities such as speaking, writing, walking, or even maintaining balance.
Symptoms
- Involuntary muscle contractions
- Abnormal postures or twisting of limbs, neck, or trunk
- Pain due to muscle overactivity
- Tremors or repetitive movements
- Speech difficulties (in laryngeal dystonia)
- Eyelid spasms (blepharospasm)
- Worsening of symptoms with stress, fatigue, or voluntary movement
Causes
Dystonia can be primary (idiopathic) or secondary due to another condition.
- Genetic mutations (e.g., DYT1 gene)
- Brain injuries (stroke, trauma, tumors)
- Neurodegenerative diseases (Parkinson’s, Huntington’s)
- Drug-induced (antipsychotics, anti-nausea medications)
- Infections or metabolic disorders
Risk Factors
- Family history of dystonia or movement disorders
- Certain medications affecting dopamine pathways
- Brain trauma or surgery
- Other neurological diseases
Complications
- Chronic pain and muscle stiffness
- Difficulty performing daily tasks
- Impaired speech or swallowing
- Social withdrawal due to visible symptoms
- Risk of falls or mobility limitations
Prevention
While dystonia cannot always be prevented, in Korea efforts focus on:
- Early neurological evaluation for movement symptoms
- Avoidance of triggering medications where possible
- Regular monitoring in patients with Parkinson’s or related conditions
- Genetic counseling for families with hereditary dystonia
Treatment Options in Korea
Diagnosis
- Neurological examination by movement disorder specialists
- MRI or CT scans to detect brain abnormalities
- Genetic testing in suspected hereditary dystonia cases
- Electromyography (EMG) to assess abnormal muscle activity
Medical Treatments
- Oral medications (anticholinergics, benzodiazepines, baclofen)
- Botulinum toxin (Botox) injections – highly effective for focal dystonia
- Muscle relaxants and anti-seizure drugs
Surgical & Advanced Therapies
- Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS): Widely available in Korea at top neurosurgical centers; electrodes implanted in the basal ganglia help reduce symptoms.
- Intrathecal baclofen therapy for severe cases.
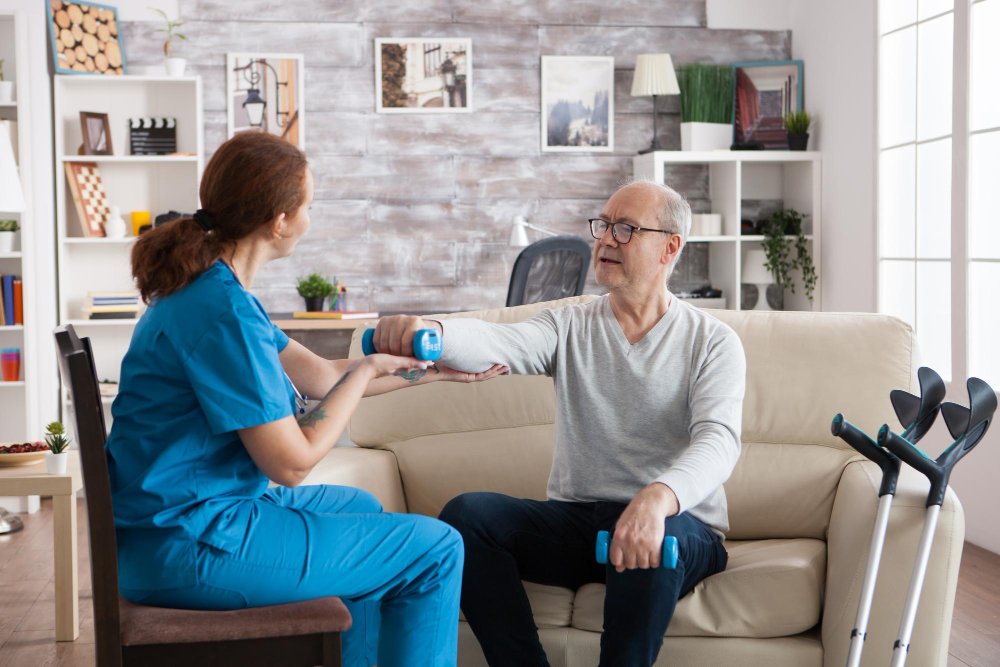
- Neuro-rehabilitation programs including physiotherapy and occupational therapy.
Rehabilitation & Support
- Speech therapy for laryngeal dystonia
- Physical therapy to reduce stiffness and improve mobility
- Psychological counseling for coping with chronic illness
- Patient support groups available in Seoul and major cities