Overview
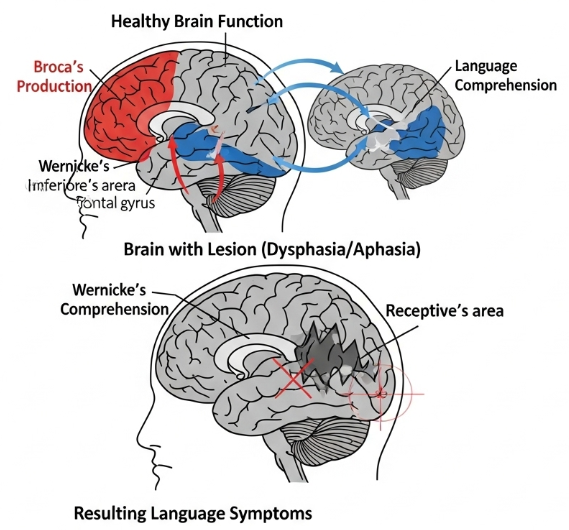
Dysphasia is a language disorder caused by damage to the brain areas responsible for communication, most commonly after a stroke, head injury, or brain disease. Unlike dysarthria (a speech motor disorder), dysphasia specifically affects language comprehension and expression.
In Korea, dysphasia is often seen in patients recovering from stroke, which is a leading cause of disability. Korean hospitals provide state-of-the-art neuroimaging, advanced stroke care, and intensive speech therapy programs to help patients regain communication skills.
What is Dysphasia?
Dysphasia is a neurological condition in which a person has difficulty understanding or using language, though intelligence remains intact. It can affect:
- Expressive language (difficulty speaking or writing)
- Receptive language (difficulty understanding spoken or written language)
- Or both (global dysphasia)
It is usually caused by damage to the left hemisphere of the brain, particularly the Broca’s or Wernicke’s area.
Symptoms
- Difficulty finding the right words
- Speaking in short, incomplete sentences
- Using incorrect or nonsensical words
- Difficulty understanding spoken language
- Problems with reading or writing
- Frustration or emotional distress when trying to communicate
Causes
- Stroke (most common cause in Korea)
- Traumatic brain injury
- Brain tumors
- Neurodegenerative diseases (e.g., Alzheimer’s disease, frontotemporal dementia)
- Brain infections or inflammation
Risk Factors
- Age (older adults at higher risk due to stroke prevalence)
- Hypertension and diabetes
- High cholesterol
- History of smoking or alcohol use
- Family history of stroke or neurological disease
Complications
- Social isolation and withdrawal
- Depression and anxiety
- Difficulty in professional and personal communication
- Reduced quality of life
- Dependence on caregivers
Prevention
- Preventing strokes through blood pressure, diabetes, and cholesterol management
- Healthy lifestyle (balanced diet, regular exercise, no smoking, limited alcohol)
- Early treatment of head injuries and infections
- Regular medical checkups for at-risk patients
Treatment Options in Korea
Diagnosis
- Brain MRI or CT scans to identify the cause (e.g., stroke, tumor)
- Neuropsychological and language assessment
- Blood tests to rule out metabolic or infectious causes
Medical Treatments
- Immediate stroke treatment (clot-busting drugs, thrombectomy) when applicable
- Medications to manage underlying conditions (hypertension, cholesterol, seizures)
- Neuroprotective drugs in select cases
Rehabilitation and Support
- Speech and language therapy (SLT): intensive programs in specialized Korean rehabilitation centers
- Computer-assisted language training tools widely available in Korea
- Group therapy sessions to improve social communication
- Family and caregiver education for better support at home
Advanced Therapies in Korea
- Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) for language recovery (available in research hospitals)
- Robotic and AI-assisted rehabilitation tools to enhance therapy outcomes