Overview
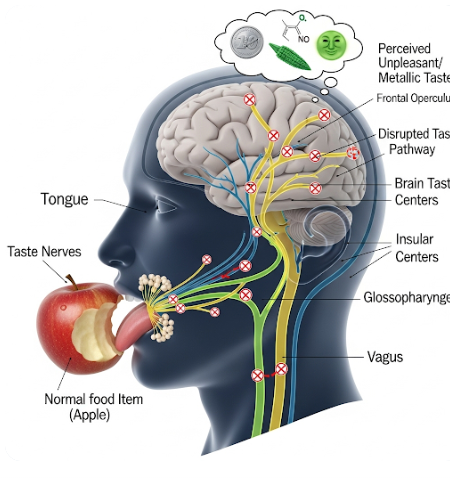
Dysgeusia is a disorder characterized by a distortion or alteration in the sense of taste. In South Korea, this condition is increasingly recognized due to its impact on nutrition, appetite, and quality of life. Dysgeusia can result from various underlying health issues, medications, or lifestyle factors. Early identification and management can help restore taste function and prevent nutritional deficiencies.
What is Dysgeusia?
Dysgeusia refers to any change in taste perception, including persistent metallic, bitter, salty, or sour tastes, or reduced taste sensitivity. It can affect one or more taste sensations and may occur temporarily or chronically.
Symptoms
Common symptoms include:
- Distorted perception of taste (metallic, bitter, or unusual taste)
- Reduced ability to taste foods (hypogeusia)
- Complete loss of taste (ageusia)
- Unpleasant taste in the mouth unrelated to food
- Changes in appetite or food preferences
Causes
Dysgeusia can be caused by:
- Medications such as antibiotics, antihypertensives, or chemotherapy drugs
- Nutritional deficiencies, especially zinc or vitamin B12
- Oral or dental issues (e.g., infections, poor oral hygiene)
- Neurological disorders affecting taste pathways
- Infections, including COVID-19 or other viral illnesses
- Exposure to toxins or chemicals
Risk Factors
Factors increasing the likelihood of dysgeusia include:
- Advanced age
- Smoking or excessive alcohol use
- Chronic illnesses such as diabetes or kidney disease
- Use of multiple medications simultaneously
- Poor oral health
Complications
Untreated dysgeusia may lead to:
- Decreased appetite and reduced food intake
- Weight loss or malnutrition
- Psychological effects such as frustration or anxiety
- Reduced quality of life due to dietary restrictions
Prevention
Preventive measures focus on maintaining oral and overall health:
- Regular dental checkups and good oral hygiene
- Adequate nutrition and vitamin supplementation
- Avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption
- Monitoring medications for taste-related side effects
Treatment Options in Korea
In South Korea, management of dysgeusia involves a combination of medical, nutritional, and supportive approaches:
Medical Management:
- Adjusting or substituting medications causing taste disturbances
- Treating underlying medical conditions
- Zinc or vitamin supplementation if deficiencies are identified
Supportive Care:
- Oral hygiene optimization, including mouth rinses and dental care
- Flavor enhancement strategies to improve food palatability
- Dietary counseling to maintain adequate nutrition
Specialized Care:
- ENT (ear, nose, and throat) and neurology departments in Korean hospitals provide evaluation for taste disorders
- Multidisciplinary care may include nutritionists, dentists, and neurologists to address underlying causes and improve taste perception
With early diagnosis and targeted interventions in Korea, individuals with dysgeusia can restore taste function, maintain proper nutrition, and improve overall quality of life.