Overview
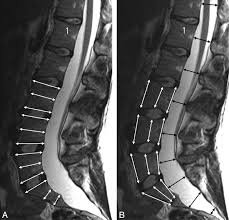
Dural ectasia is a condition characterized by the widening or ballooning of the dural sac surrounding the spinal cord. In South Korea, it is most commonly associated with connective tissue disorders, such as Marfan syndrome or Ehlers-Danlos syndrome. While often asymptomatic, dural ectasia can lead to back pain, neurological issues, and postural problems if left unmonitored.
What is Dural Ectasia?
Dural ectasia involves the expansion of the dural sac and, in some cases, the nerve root sleeves. It typically affects the lumbar and sacral regions of the spine. The condition may be congenital or develop over time due to underlying connective tissue weakness.
Symptoms
Symptoms vary based on severity and location and may include:
- Lower back pain
- Leg pain or numbness
- Sciatica-like symptoms
- Postural abnormalities or spinal curvature
- Headaches, particularly when standing
- Urinary or bowel dysfunction in severe cases
Causes
The primary causes of dural ectasia include:
- Connective tissue disorders such as Marfan syndrome, Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, or neurofibromatosis
- Increased cerebrospinal fluid pressure
- Degenerative changes in the spine
- Congenital weakness of the dural sac
Risk Factors
Factors that increase the likelihood of dural ectasia include:
- Genetic connective tissue disorders
- Family history of spinal or dural abnormalities
- Age-related spinal degeneration
- History of spinal trauma
Complications
Untreated dural ectasia may result in:
- Progressive neurological deficits
- Chronic back and leg pain
- Spinal instability or increased curvature
- Bladder or bowel dysfunction in severe cases
Prevention
Since dural ectasia is often genetic, prevention focuses on:
- Regular monitoring in patients with connective tissue disorders
- Early detection through imaging for at-risk individuals
- Maintaining spinal health through exercise and posture management
Treatment Options in Korea
Management of dural ectasia in South Korea includes monitoring, symptom management, and surgical intervention in severe cases:
Medical Management:
- Pain relief with NSAIDs or other analgesics
- Physical therapy to strengthen core muscles and improve posture
- Monitoring of neurological symptoms
Surgical Intervention:
- Rarely required, but may involve stabilization or repair of affected spinal segments
- Neurosurgical intervention for severe nerve compression or instability
Specialized Care:
- Orthopedic and neurosurgery departments in Korean hospitals provide diagnostic imaging (MRI, CT scans) and treatment
- Multidisciplinary care with physiotherapists and neurologists ensures long-term management and quality of life
With early recognition and proper monitoring in Korea, dural ectasia can often be managed conservatively, allowing patients to maintain mobility and minimize complications.