Overview
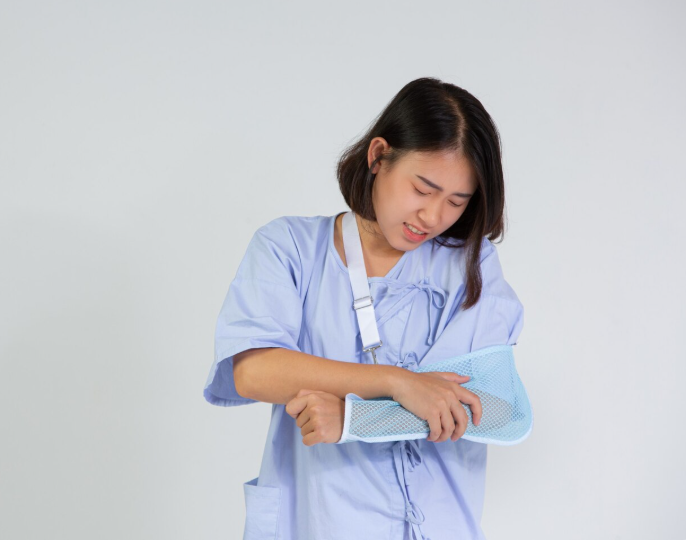
A dislocated shoulder occurs when the upper arm bone (humerus) is forced out of the shoulder socket, causing severe pain and restricted movement. In Korea, orthopedic specialists and sports medicine clinics provide rapid diagnosis, reduction procedures, and rehabilitation programs to restore shoulder function and prevent recurrence.
What is a Dislocated Shoulder?
A dislocated shoulder is an orthopedic injury where the humeral head is displaced from the glenoid cavity of the shoulder joint. It often results from trauma, falls, or sports injuries, and can involve damage to ligaments, tendons, or nerves around the shoulder.
Symptoms
- Intense shoulder pain
- Visible deformity or “out-of-place” shoulder
- Swelling or bruising
- Limited range of motion
- Numbness or tingling down the arm
- Muscle weakness around the shoulder
Causes
- Sports injuries (football, basketball, skiing)
- Falls on an outstretched arm
- Traffic accidents or sudden impact
- Seizures or electric shocks causing violent muscle contraction
Risk Factors
- History of previous shoulder dislocations
- Participation in contact sports
- Weak or loose shoulder ligaments
- Occupations requiring repetitive overhead movements
- Age (young adults are more prone)
Complications
- Recurrent shoulder dislocations
- Rotator cuff tears
- Nerve or blood vessel injury
- Chronic pain or arthritis in the shoulder joint
- Limited shoulder mobility
Prevention
- Strengthen shoulder muscles with targeted exercises
- Avoid high-risk activities or use protective gear
- Practice proper techniques in sports
- Warm up before physical activity
- Prompt treatment of minor shoulder injuries to prevent instability
Treatment Options in Korea
Diagnosis
- Physical examination by an orthopedic specialist
- X-ray or MRI to confirm dislocation and assess ligament or tendon damage
- CT scan in complex or recurrent cases
Medical Treatments
- Closed reduction: manual repositioning of the shoulder
- Pain management with medications or anti-inflammatories
- Immobilization using a sling for several weeks
- Physical therapy to regain strength and range of motion
Surgical or Advanced Therapies
- Arthroscopic surgery for recurrent dislocations or ligament injuries
- Rotator cuff repair if tendon damage is present
- Reconstructive surgery for severe or complex shoulder injuries
Rehabilitation and Support
- Gradual physiotherapy focusing on strength, flexibility, and stabilization
- Occupational therapy for return to daily activities
- Patient education on post-injury precautions
- Long-term follow-up for recurrent cases