Overview
Discoid Lupus Erythematosus (DLE) is a chronic autoimmune skin condition that primarily affects the face, scalp, and ears, leading to scaly, disc-shaped lesions. In Korea, dermatologists provide advanced diagnostic tools, topical and systemic treatments, and patient education to manage the disease and prevent scarring.
What is Discoid Lupus Erythematosus?
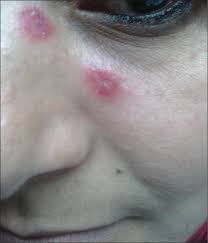
DLE is a form of cutaneous lupus characterized by localized skin inflammation. Unlike systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), DLE mainly affects the skin and rarely involves internal organs. The condition often leads to permanent scarring, pigment changes, and hair loss if left untreated.
Symptoms
- Round, red, scaly skin lesions
- Thickened patches that may leave scars
- Hair loss in affected areas (especially scalp)
- Skin discoloration (hypopigmentation or hyperpigmentation)
- Sensitivity to sunlight (photosensitivity)
- Mild itching or burning sensation
Causes
- Autoimmune reaction causing the immune system to attack skin cells
- Genetic predisposition
- Environmental triggers such as sun exposure
- Hormonal factors may contribute in some cases
Risk Factors
- Women are more commonly affected than men
- Age between 20–40 years
- Family history of lupus or autoimmune disorders
- Prolonged exposure to sunlight
- Certain medications that can trigger lupus-like reactions
Complications
- Permanent scarring and disfigurement
- Hair loss (alopecia) if scalp is affected
- Skin infections in damaged areas
- Rare progression to systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)
- Psychological impact due to cosmetic changes
Prevention
- Avoid excessive sun exposure and use broad-spectrum sunscreen
- Wear protective clothing and hats outdoors
- Regular skin examinations for early detection
- Prompt treatment of lesions to prevent scarring
- Avoid medications that may trigger lupus flare-ups
Treatment Options in Korea
Diagnosis
- Skin biopsy to confirm characteristic histological findings
- Blood tests to rule out systemic lupus involvement
- Phototesting to assess sun sensitivity
Medical Treatments
- Topical corticosteroids to reduce inflammation
- Calcineurin inhibitors (e.g., tacrolimus) for sensitive areas
- Systemic medications (hydroxychloroquine, immunosuppressants) for severe or widespread lesions
- Antimalarial drugs like hydroxychloroquine for skin flare control
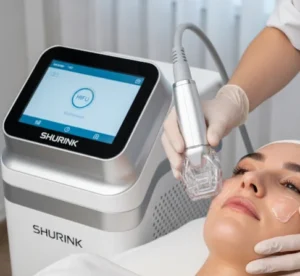
Surgical or Advanced Therapies
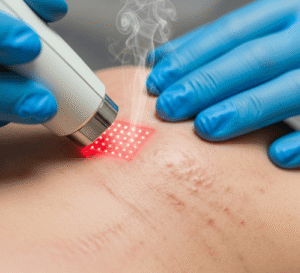
- Laser therapy for pigment correction or scar reduction
- Surgical options for reconstructive purposes in severe scarring
- Hair restoration treatments if alopecia occurs
Rehabilitation and Support
- Regular follow-up with dermatologists for early intervention
- Psychological counseling for coping with cosmetic changes
- Education on sun protection and disease management
- Support groups for patients with chronic autoimmune skin conditions