Overview
Gestational diabetes is a form of diabetes diagnosed during pregnancy, affecting how the body processes glucose. In Korea, routine prenatal screening helps detect gestational diabetes early, reducing risks for both mother and baby. Major hospitals and obstetrics clinics provide comprehensive care for management and follow-up.
What is Gestational Diabetes?
Gestational diabetes occurs when pregnant women develop high blood sugar levels due to insulin resistance induced by pregnancy hormones. It typically appears in the second or third trimester and usually resolves after delivery, though it increases the risk of developing Type 2 diabetes later in life.
Symptoms
- Often asymptomatic, detected during prenatal screening
- Increased thirst
- Frequent urination
- Fatigue
- Blurred vision (rare)
- Recurrent infections, such as urinary tract infections
Causes
- Pregnancy hormones interfere with insulin function
- Pancreas cannot produce enough insulin to overcome resistance
- Genetic predisposition and family history of diabetes
- Overweight or obesity before pregnancy
Risk Factors
- Age over 25 years
- Family history of diabetes
- Overweight or obese before pregnancy
- Previous gestational diabetes or large baby (>4 kg)
- Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
Complications
- Increased risk of high birth weight (macrosomia)
- Birth complications, such as cesarean delivery
- Hypoglycemia in newborns
- Preeclampsia in mothers
- Increased risk of Type 2 diabetes postpartum
Prevention
- Maintain healthy weight before pregnancy
- Balanced diet with complex carbohydrates and fiber
- Regular physical activity before and during pregnancy
- Prenatal screening for high-risk women
Treatment Options in Korea
- Diagnosis
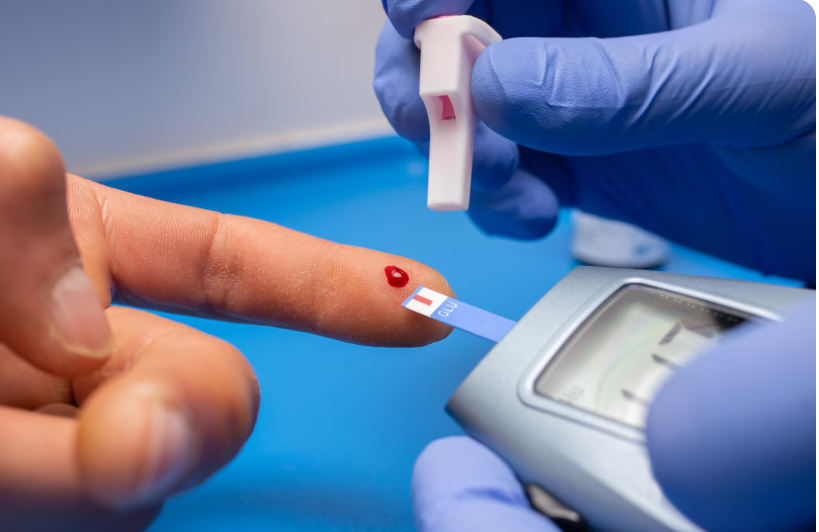
- Glucose challenge test (GCT) between 24–28 weeks
- Oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) for confirmation
- Medical Treatments
- Dietary modifications tailored by nutritionists
- Blood sugar monitoring at home
- Insulin therapy if lifestyle management is insufficient
- Regular obstetric follow-up to monitor fetal growth
- Rehabilitation & Support
- Nutritional counseling during and after pregnancy
- Education on postpartum glucose monitoring
- Guidance on lifestyle changes to prevent Type 2 diabetes