Overview
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) is a blood clot formation in the deep veins, usually in the legs. It can be a serious condition because clots may travel to the lungs, causing a pulmonary embolism (PE). In Korea, DVT is managed through early detection, anticoagulation therapy, and advanced interventions in hospitals like Seoul National University Hospital, Asan Medical Center, and Samsung Medical Center. Awareness of risk factors and preventive measures is emphasized to reduce complications.
What is Deep Vein Thrombosis?
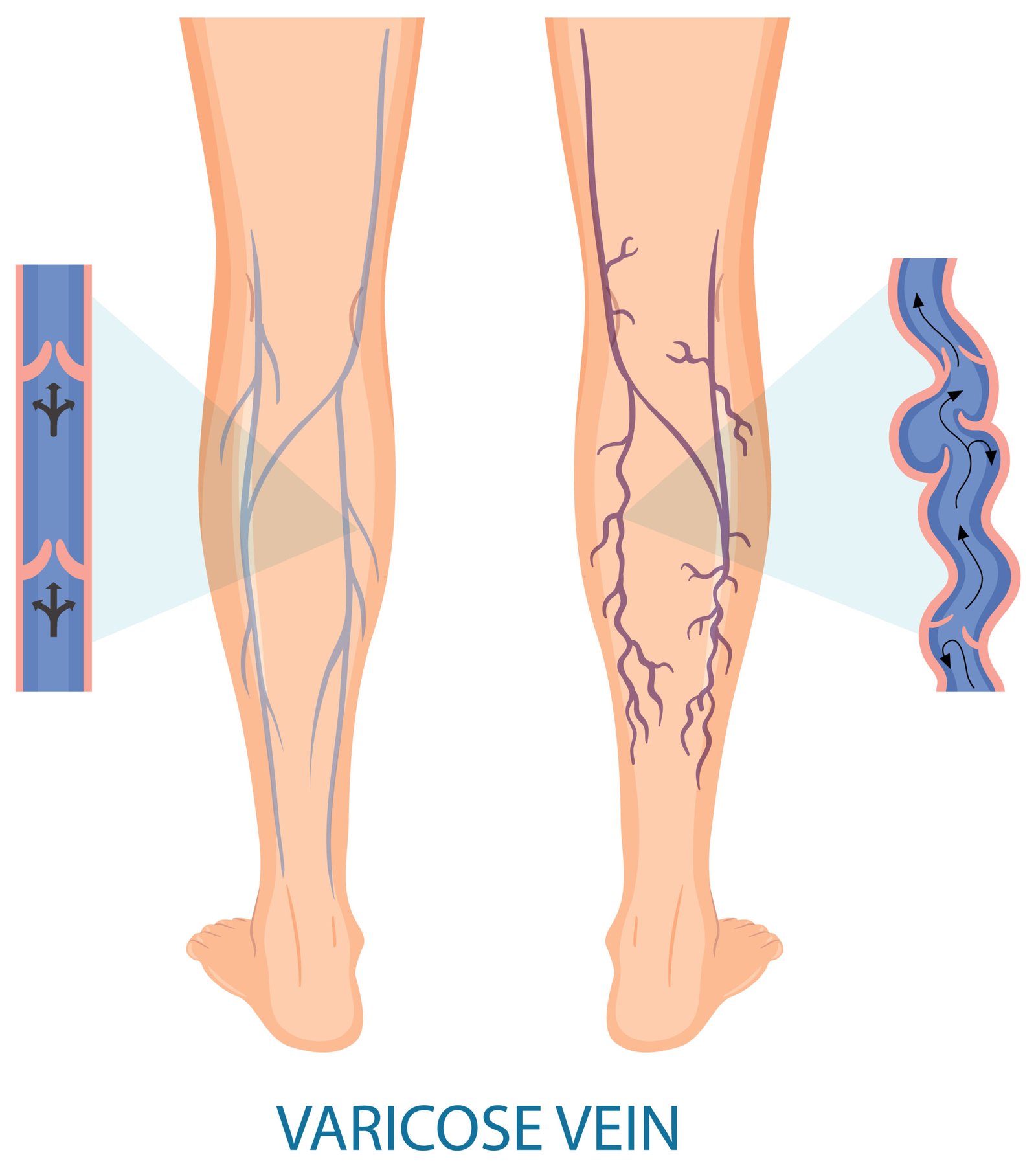
DVT is the development of a blood clot in a deep vein, most commonly in the calf or thigh. It can occur due to slow blood flow, vessel injury, or hypercoagulable states. While some patients may be asymptomatic, DVT can progress to life-threatening complications if untreated.
Symptoms
- Swelling in one leg (or arm in rare cases)
- Pain or tenderness, often starting in the calf
- Warmth and redness over the affected area
- Leg heaviness or cramping
- Visible surface veins in some cases
Causes
- Prolonged immobility (long flights, bed rest)
- Surgery, particularly orthopedic or abdominal surgery
- Trauma or injury to veins
- Cancer or cancer treatments
- Inherited blood clotting disorders (thrombophilia)
- Pregnancy and postpartum period
Risk Factors
- Age over 60 years
- Obesity or overweight
- Smoking
- Previous DVT or family history of blood clots
- Hormone replacement therapy or oral contraceptives
- Prolonged sitting or immobility
- Chronic medical conditions such as heart disease or diabetes
Complications
- Pulmonary embolism (PE) – a life-threatening blockage in the lungs
- Post-thrombotic syndrome causing chronic leg pain, swelling, and skin changes
- Recurrence of blood clots
- Venous ulcers in severe chronic cases
Prevention
- Regular movement during long periods of sitting (e.g., flights or office work)
- Compression stockings for at-risk individuals
- Maintaining a healthy weight and active lifestyle
- Hydration and avoidance of smoking
- Anticoagulant therapy for high-risk patients under medical supervision
- Postoperative mobilization and physiotherapy
Treatment Options in Korea
Korean hospitals provide comprehensive management for DVT, focusing on clot prevention, dissolution, and complication prevention.
- Diagnosis
- Doppler ultrasound to visualize clot formation
- D-dimer blood test to detect clotting activity
- Venography in complex cases
- Blood tests to assess clotting disorders
- Medical Treatments
- Anticoagulants (blood thinners) such as heparin, warfarin, or DOACs
- Thrombolytic therapy in severe cases to dissolve clots
- Pain management and leg elevation
- Surgical and Interventional Treatments
- Catheter-directed thrombolysis for extensive clots
- Inferior vena cava (IVC) filter placement in patients who cannot take anticoagulants
- Specialized Hospitals in Korea
- Seoul National University Hospital – Vascular medicine and interventional radiology
- Asan Medical Center – Comprehensive thromboembolism care
- Samsung Medical Center – Advanced diagnostics, treatment, and rehabilitation
- Regional clinics for anticoagulation monitoring and follow-up
- Long-Term Follow-Up
- Regular monitoring of anticoagulant therapy and blood clotting status
- Ultrasound follow-up for clot resolution
- Education on lifestyle modifications to prevent recurrence
- Management of post-thrombotic syndrome with compression therapy and physical therapy