Overview
A cyst is a closed sac-like structure filled with liquid, semi-solid, or gaseous material that can develop in any part of the body. Most cysts are benign, but depending on their size, location, and type, they may cause pain, discomfort, or complications. South Korea provides advanced diagnostic imaging and minimally invasive treatments for a wide range of cysts.
What is a Cyst?
A cyst is an abnormal fluid-filled pocket in the body that can occur in organs, tissues, or under the skin. Common types include:
- Epidermoid or sebaceous cysts: Develop under the skin, often on the face, neck, or back.
- Ovarian cysts: Arise from the ovaries in women.
- Ganglion cysts: Typically appear on the wrists or hands.
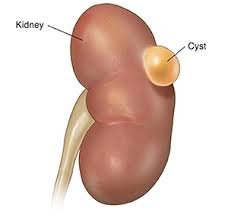
- Kidney or liver cysts: Often found incidentally during imaging and usually asymptomatic.
Cysts may remain unnoticed or lead to pain, infection, or obstruction depending on their size and location.
Symptoms
Symptoms vary according to cyst type and location:
General symptoms:
- Noticeable lump or swelling
- Tenderness or pain if inflamed or infected
- Redness or warmth over the area
- Pressure on nearby organs (e.g., urinary problems with ovarian cysts)
Ovarian cyst symptoms:
- Pelvic pain or bloating
- Irregular menstrual periods
- Discomfort during intercourse
Ganglion cyst symptoms:
- Visible lump on the wrist or hand
- Pain or restricted movement if large
Causes
Cysts can form due to:
- Blocked ducts or glands (sebaceous or ganglion cysts)
- Genetic conditions or developmental anomalies
- Chronic inflammation or infection
- Fluid accumulation in organs such as kidneys or liver
Risk Factors
- Female gender (for ovarian cysts)
- Age (middle-aged adults for sebaceous cysts, women of reproductive age for ovarian cysts)
- History of prior cysts
- Chronic skin conditions or infections
Complications
- Infection of the cyst leading to abscess formation
- Rupture causing sudden pain or internal bleeding (especially ovarian cysts)
- Pressure effects on nearby tissues or organs
- Rarely, malignant transformation in certain cyst types
Prevention
- Regular health check-ups and imaging for early detection
- Good hygiene to prevent skin cyst infections
- Prompt treatment of infections or blockages in ducts or glands
- Awareness of symptoms like sudden pain, swelling, or abnormal lumps
Treatment Options in Korea
South Korea offers highly specialized care for cysts with modern medical facilities and minimally invasive procedures:
- Diagnosis
- Ultrasound: Common for ovarian and superficial cysts
- CT scan or MRI: Detailed imaging for internal or complex cysts
- Blood tests: To rule out infection or malignancy in some cysts
- Monitoring
- Small, asymptomatic cysts may be monitored periodically
- Imaging follow-up to check for changes in size or characteristics
- Medication
- Antibiotics for infected cysts
- Pain management for symptomatic relief
- Procedures & Surgery
- Aspiration or drainage: Minimally invasive removal of cyst fluid
- Excision surgery: Complete removal of cysts, often done laparoscopically for ovarian or internal cysts
- Sclerotherapy: Injection to prevent recurrence of certain cysts
- Post-Treatment Care
- Follow-up imaging to ensure no recurrence
- Wound care and infection prevention for surgical sites
- Lifestyle advice for chronic or recurrent cysts