Overview
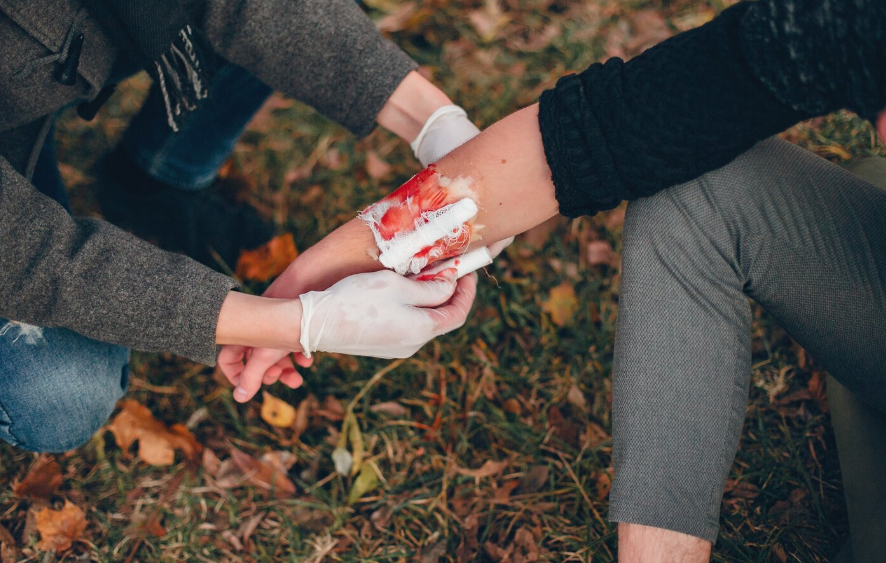
A crush injury occurs when a part of the body is subjected to extreme force or pressure, often trapped between heavy objects. This type of trauma can damage muscles, bones, blood vessels, and nerves. Severe crush injuries may lead to life-threatening complications like rhabdomyolysis, kidney failure, or shock. South Korea offers advanced trauma care and surgical interventions to manage crush injuries effectively.
What is a Crush Injury?
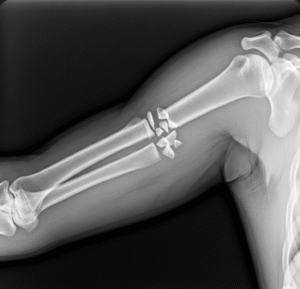
A crush injury is a traumatic condition resulting from prolonged compression of body parts. Commonly affected areas include the arms, legs, and torso. The severity depends on the duration of compression, the weight of the object, and the body part involved.
Crush injuries may also result in crush syndrome, a systemic condition caused by muscle breakdown and release of toxins into the bloodstream.
Symptoms
Symptoms may vary depending on the severity and location of the injury:
Local Symptoms:
- Severe pain at the injury site
- Swelling and bruising
- Skin discoloration (pale, blue, or dark)
- Numbness or tingling
- Muscle weakness or paralysis
Systemic Symptoms (Crush Syndrome):
- Dark or reddish urine (myoglobinuria)
- Low blood pressure (hypotension)
- Rapid heart rate (tachycardia)
- Confusion or altered mental status
- Electrolyte imbalances, leading to cardiac arrhythmias
Causes
- Traffic accidents
- Industrial or construction site accidents
- Earthquakes, landslides, or building collapses
- Heavy machinery accidents
- Falling debris or objects
Risk Factors
- Occupations involving heavy machinery or construction work
- Natural disasters (earthquakes, landslides)
- Poor workplace safety measures
- Delayed rescue after entrapment
Complications
- Rhabdomyolysis: Breakdown of muscle tissue leading to kidney damage
- Acute kidney injury
- Compartment syndrome: Increased pressure in muscle compartments causing nerve and tissue damage
- Infections at the injury site
- Shock due to blood loss or systemic toxin release
- Amputation in severe cases
Prevention
- Adhering to workplace safety protocols
- Using protective equipment in hazardous environments
- Immediate evacuation in natural disasters
- Training in proper lifting and handling techniques
- Emergency preparedness and rapid first aid
Treatment Options in Korea
South Korea provides advanced trauma care, including surgical, medical, and rehabilitative management of crush injuries.
1. Emergency Care
- Immediate assessment and stabilization
- Airway, breathing, and circulation management
- Intravenous fluids to prevent kidney failure
2. Surgical Intervention
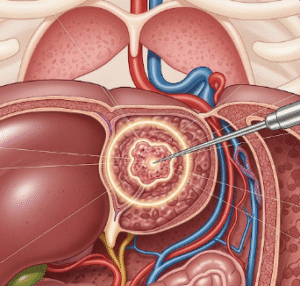
- Fasciotomy for compartment syndrome
- Debridement of damaged tissue
- Repair of bones, blood vessels, and nerves
- Amputation in severe, non-salvageable cases
3. Medication
- Pain management (analgesics)
- Antibiotics to prevent infection
- Electrolyte correction to prevent cardiac complications
4. Monitoring & Supportive Care
- Kidney function monitoring (for rhabdomyolysis)
- Continuous cardiac monitoring
- Physical therapy for mobility and function recovery
5. Rehabilitation
- Occupational therapy to restore daily function
- Psychological support for trauma-related stress
- Long-term follow-up to monitor complications and recovery