Overview
Crohn’s disease is a chronic inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) that affects the digestive tract, causing inflammation and damage to the lining of the gastrointestinal system. It can involve any part of the digestive tract, from the mouth to the anus, but most commonly affects the small intestine and colon. In Korea, awareness and treatment of Crohn’s disease have grown significantly, with advanced diagnostic tools and multidisciplinary treatment options available.
What is Crohn’s Disease?
Crohn’s disease is an autoimmune condition where the immune system mistakenly attacks the digestive tract, leading to chronic inflammation. It is different from ulcerative colitis because Crohn’s can affect any part of the digestive tract and often involves deeper layers of the bowel wall. The disease tends to have periods of remission and flare-ups.
Symptoms
- Abdominal pain and cramping
- Persistent diarrhea
- Fatigue and weakness
- Weight loss and poor appetite
- Fever during flare-ups
- Blood or mucus in stool
- Perianal disease (fissures, fistulas, or abscesses in some patients)
Causes
The exact cause is unknown, but contributing factors include:
- Immune system dysfunction
- Genetic predisposition (family history of IBD)
- Environmental triggers (diet, smoking, infections)
- Imbalance of gut microbiota
Risk Factors
- Family history of Crohn’s or ulcerative colitis
- Smoking (significantly increases risk and severity)
- Young adults (most cases diagnosed before age 30)
- Living in urban or industrialized areas
- Previous gastrointestinal infections
Complications
- Bowel strictures or obstructions
- Fistulas (abnormal connections between organs)
- Malnutrition and vitamin/mineral deficiencies
- Increased risk of colon cancer
- Abscesses and severe infections
- Growth delays in children
Prevention
While Crohn’s disease cannot be completely prevented, steps to reduce flare-ups include:
- Avoiding smoking and secondhand smoke
- Eating a balanced, low-irritant diet
- Stress management techniques
- Regular medical checkups and colonoscopies for monitoring
- Early treatment of infections or gastrointestinal symptoms
Treatment Options in Korea
Korea offers modern and effective treatment strategies for Crohn’s disease, combining medication, nutrition, and sometimes surgery.
1. Diagnosis
- Colonoscopy with biopsy (gold standard)
- Imaging (CT enterography, MRI enterography) for deeper tissue evaluation
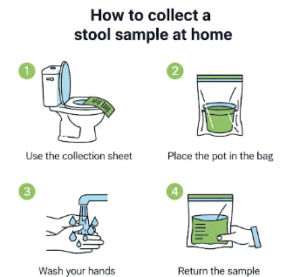
- Blood tests (inflammation markers) and stool studies
2. Medical Management
- Anti-inflammatory drugs: Aminosalicylates for mild disease
- Corticosteroids: Short-term control of flare-ups
- Immunosuppressants: Azathioprine, methotrexate to reduce immune response
- Biologic therapies: Anti-TNF agents (infliximab, adalimumab) and newer biologics
- Antibiotics: For fistulas and abscesses
3. Nutrition and Lifestyle
- Special diets and nutritional supplements when needed
- Counseling with dietitians experienced in IBD care
4. Surgical Treatment
- Surgery may be required for complications like strictures, perforations, or severe disease unresponsive to medication. Korean hospitals have advanced laparoscopic and minimally invasive surgery options.
5. Long-term Monitoring
- Regular follow-up with gastroenterologists
- Screening for complications like colon cancer
- Psychological support and patient education programs