Overview
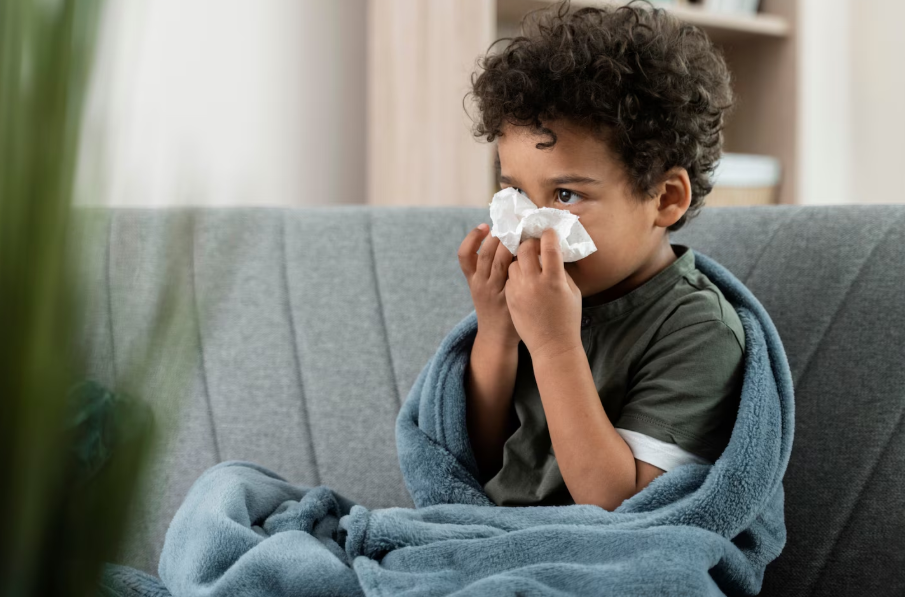
Coughs and colds are among the most common illnesses in children, usually caused by viral infections of the upper respiratory tract. While most cases are mild and self-limiting, frequent colds can affect a child’s comfort, sleep, and school attendance. In South Korea, pediatric care for coughs and colds is advanced, with access to clinical assessment, symptomatic treatment, and parental guidance for home care.
What are Coughs and Colds?
A cold is a mild viral infection affecting the nose, throat, and upper airways. The accompanying cough is often a reflex to clear mucus and irritants from the respiratory tract. Most cases in children are caused by rhinoviruses, but other viruses like adenovirus, respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), or influenza can also be responsible.
Symptoms
- Runny or stuffy nose
- Sneezing
- Mild fever (occasionally)
- Sore throat
- Persistent or intermittent cough
- Fatigue or irritability
- Loss of appetite
- Watery eyes
Causes
- Viral infections (most common)
- Exposure to infected individuals in schools or daycare
- Weakened immune system or seasonal vulnerability
- Allergic triggers can mimic or worsen symptoms
Risk Factors
- Age under 6 years (especially toddlers in daycare)
- Frequent contact with other children
- Seasonal changes, particularly autumn and winter
- Pre-existing conditions like asthma or allergies
- Exposure to secondhand smoke
Complications
- Middle ear infection (otitis media)
- Sinusitis
- Asthma exacerbation in susceptible children
- Rarely, pneumonia or bronchiolitis
- Sleep disturbances and dehydration in severe cases
Prevention
- Regular handwashing and hygiene practices
- Avoid close contact with sick individuals
- Maintain vaccination schedules (influenza vaccine annually)
- Healthy diet and adequate sleep to support immunity
- Avoid exposure to tobacco smoke
Treatment Options in Korea
South Korea provides comprehensive pediatric care for children with coughs and colds:
- Clinical Assessment
- Pediatric clinics assess for viral versus bacterial infection
- Identification of risk factors or underlying conditions
- Symptomatic Treatment
- Fever management with acetaminophen or ibuprofen
- Saline nasal sprays or drops for congestion
- Humidifiers to ease throat irritation
- Cough syrups and lozenges for children above recommended age
- Medications (if necessary)
- Antibiotics only if bacterial infection is confirmed
- Antihistamines for allergic symptoms
- Monitoring and Follow-Up
- Observation for worsening symptoms such as high fever, breathing difficulty, or persistent cough
- Pediatricians provide guidance on home care and hydration
- Emergency Care
- Severe breathing difficulties, dehydration, or prolonged high fever require hospital evaluation
- Hospitals in Korea have pediatric emergency services and supportive therapies, including oxygen if needed