Overview
Congenital nevi are pigmented birthmarks or moles present at birth. They develop due to an increased number of melanocytes (pigment-producing cells) in the skin. These lesions vary in size, color, and shape and may grow as the child grows. While most congenital nevi are harmless, some may carry a small risk of developing into melanoma (skin cancer). In Korea, dermatology and plastic surgery clinics provide advanced diagnostic and treatment options, including laser therapy and surgical removal.
What is Congenital Nevi?
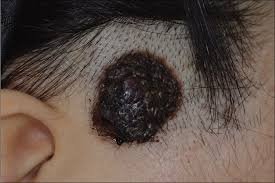
A congenital nevus is a benign (non-cancerous) pigmented skin lesion present at birth or appearing shortly after. It can be small, medium, or large (giant) in size. Large congenital nevi may have more significant cosmetic concerns and a slightly higher risk of malignant transformation compared to smaller lesions.
Symptoms
- Dark brown, black, or tan patch of skin present at birth
- Can be flat, raised, or hairy
- Shape can be round, oval, or irregular
- Grows proportionally as the child grows
- Usually painless, but itching or changes in texture/color may occur
Causes
- Caused by genetic changes during fetal development that affect melanocyte formation
- Not inherited in most cases (usually sporadic)
- Related to overgrowth of pigment-producing cells in the skin
Risk Factors
- Large or giant congenital nevi have a higher risk of complications
- Family history of unusual skin lesions or melanoma (rarely relevant)
- Sun exposure may darken the lesion or cause changes
Complications
- Cosmetic concerns or psychological impact due to appearance
- Skin irritation or trauma to the lesion
- Small risk of melanoma (especially in larger nevi)
- Rarely, giant nevi may be associated with neurologic involvement (neurocutaneous melanosis)
Prevention
- Cannot be prevented since they occur before birth
- Skin care and sun protection are important to reduce irritation and risk of changes
- Regular dermatological follow-up for monitoring
Treatment Options in Korea
Korean dermatology and plastic surgery clinics offer advanced and cosmetic-focused treatments for congenital nevi:
1. Diagnosis
- Physical examination and dermoscopy to assess features
- Digital mole mapping and photography for monitoring changes
- Skin biopsy if suspicious changes occur
2. Non-Surgical Options
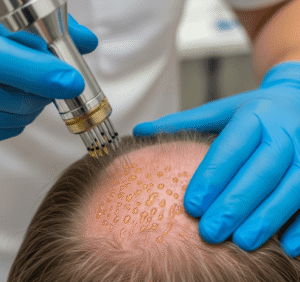
- Laser therapy (Q-switched, fractional CO₂, Alexandrite) – used for small or superficial nevi to lighten pigmentation
- Topical treatments are generally ineffective for deeper lesions
3. Surgical Treatment
- Excision (simple surgical removal) for small or medium nevi
- Serial excisions or tissue expansion for larger or giant nevi
- Skin grafting or flap surgery if large areas are removed
4. Cosmetic and Psychological Support
- Korean hospitals often provide scar-minimizing techniques and counseling for children and parents