Overview
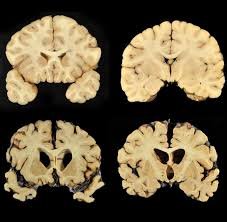
Chronic Traumatic Encephalopathy (CTE) is a progressive neurodegenerative brain disorder caused by repeated head injuries or concussions. In Korea, growing awareness in sports medicine and neurology has led to specialized evaluation, monitoring, and management for athletes and individuals at risk.
What is Chronic Traumatic Encephalopathy (CTE)?
CTE develops after multiple concussions or repetitive sub-concussive impacts, leading to abnormal tau protein accumulation in the brain. This results in cognitive, behavioral, and motor dysfunction over time. The condition is most commonly associated with contact sports, military service, and other activities involving repeated head trauma.
Symptoms
- Memory loss and cognitive decline
- Difficulty concentrating or planning
- Mood changes: depression, irritability, anxiety
- Impulse control problems or aggression
- Personality changes
- Headaches
- Motor symptoms: tremors, poor coordination, or balance difficulties
- Sleep disturbances
Causes
- Repetitive concussions or mild traumatic brain injuries (TBI)
- Contact sports (e.g., football, boxing, martial arts)
- Military blast injuries
- Accidental head injuries with repeated impact
Risk Factors
- Participation in contact or collision sports
- History of multiple concussions
- Male gender (more commonly diagnosed in studies, though women can be affected)
- Lack of protective headgear or inadequate safety measures
- Age at first exposure to repeated head trauma
Complications
- Progressive cognitive decline and dementia
- Severe mood disorders, including depression and suicidal ideation
- Behavioral problems impacting relationships and social life
- Motor dysfunction leading to mobility issues
- Reduced quality of life and independence
Prevention
- Use of protective headgear in sports and high-risk activities
- Strict concussion protocols and rest after head injuries
- Education on safe techniques in contact sports
- Limiting exposure to repetitive head trauma when possible
- Early evaluation after any head injury
Treatment Options in Korea
There is no cure for CTE, and treatment focuses on managing symptoms and improving quality of life:
- Medications:
- Antidepressants and anti-anxiety medications for mood symptoms
- Cognitive enhancers for memory and attention issues
- Pain management for headaches or related symptoms
- Therapies and interventions:
- Cognitive rehabilitation and occupational therapy
- Physical therapy for balance and motor issues
- Psychological counseling and behavioral therapy
- Support groups for patients and families
- Specialized hospitals in Korea:
- Samsung Medical Center Neurology & Rehabilitation, Seoul National University Hospital, Asan Medical Center, Severance Hospital
- Multidisciplinary teams including neurologists, psychiatrists, physiatrists, and neuropsychologists
- Follow-up care:
- Regular cognitive and neurological assessments
- Adjustment of therapy plans based on symptom progression
- Long-term support for patients and caregivers