Overview
Chronic pain is defined as persistent or recurrent pain lasting longer than three to six months, often beyond the normal healing period. In Korea, pain management and rehabilitation centers offer comprehensive evaluation and multidisciplinary treatment to improve quality of life and restore function.
What is Chronic Pain?
Chronic pain can affect any part of the body and may be neuropathic, musculoskeletal, or inflammatory in origin. Unlike acute pain, which signals injury or illness, chronic pain persists over time, sometimes without an obvious cause, and can significantly impact physical, emotional, and social well-being.
Symptoms
- Persistent pain in a specific area or widespread
- Stiffness or reduced range of motion
- Muscle tension or spasms
- Fatigue and sleep disturbances
- Mood changes, anxiety, or depression
- Sensitivity to touch or temperature (allodynia)
- Reduced ability to perform daily activities
Causes
- Musculoskeletal conditions: arthritis, back pain, fibromyalgia
- Neuropathic pain: nerve injury, diabetes, shingles
- Chronic diseases: cancer, pancreatitis, endometriosis
- Post-surgical or post-traumatic pain
- Idiopathic: no clear underlying cause in some cases
Risk Factors
- History of injury or surgery
- Chronic medical conditions such as diabetes or arthritis
- Sedentary lifestyle or poor posture
- Psychological stress or mood disorders
- Older age
- Obesity or poor physical fitness
Complications
- Reduced mobility and physical function
- Sleep disturbances and fatigue
- Emotional distress, depression, or anxiety
- Social isolation and reduced work productivity
- Dependence on pain medications if not carefully managed
Prevention
- Maintain regular physical activity and good posture
- Early treatment of injuries and medical conditions
- Weight management and healthy lifestyle habits
- Stress management techniques and mental health support
- Ergonomic adjustments in daily activities and work
Treatment Options in Korea
Chronic pain management in Korea is multidisciplinary, involving medications, therapies, and interventional procedures:
- Medications:
- Pain relievers (NSAIDs, acetaminophen)
- Neuropathic pain medications (gabapentin, pregabalin)
- Muscle relaxants or low-dose antidepressants for chronic pain modulation
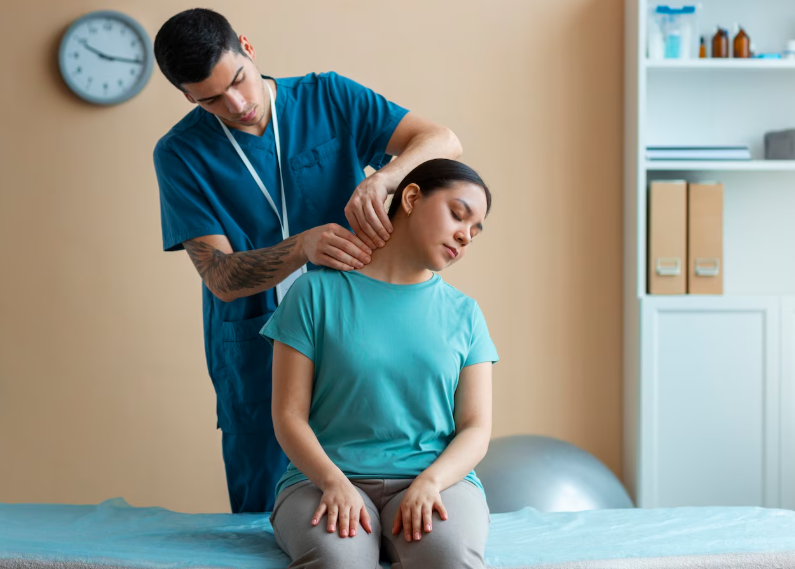
- Therapies and interventions:
- Physical therapy and exercise programs
- Occupational therapy to improve daily function
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) and psychological counseling
- Nerve blocks, epidural injections, or radiofrequency ablation for localized pain
- Acupuncture and complementary therapies
- Specialized hospitals in Korea:
- Samsung Medical Center Pain Management Clinic, Seoul National University Hospital, Asan Medical Center, Severance Hospital
- Multidisciplinary teams including pain specialists, physiatrists, psychologists, and physical therapists
- Follow-up care:
- Regular evaluation of pain levels and functional status
- Adjustment of therapies and medications as needed
- Lifestyle counseling for long-term pain control and prevention