Overview
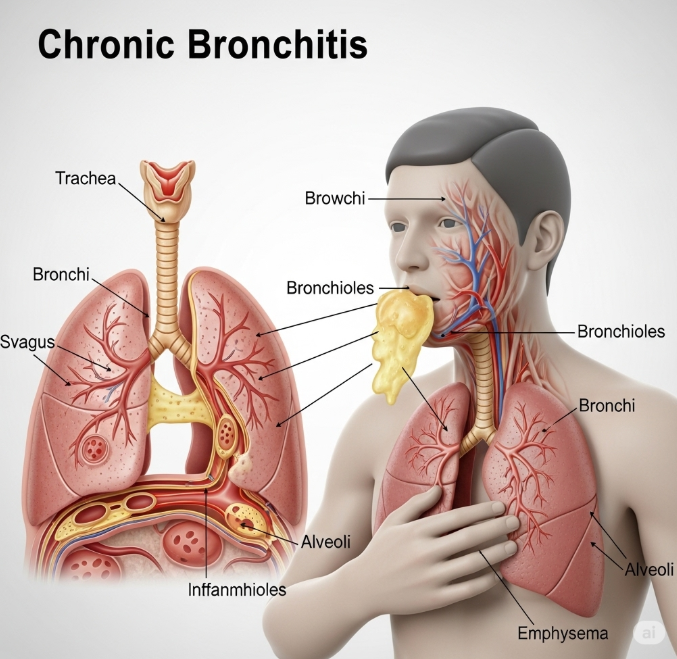
Chronic bronchitis is a long-term respiratory condition characterized by persistent inflammation of the bronchial tubes, leading to excessive mucus production and cough. It is a type of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). In Korea, pediatric and adult pulmonology centers offer diagnosis, management, and rehabilitation programs to reduce symptoms and improve lung function.
What is Chronic Bronchitis?
Chronic bronchitis involves inflammation and narrowing of the airways, which causes chronic cough with sputum production for at least three months in two consecutive years. It often develops due to smoking, air pollution, or repeated respiratory infections. If untreated, it can lead to long-term lung damage and decreased quality of life.
Symptoms
- Persistent cough, often with mucus (sputum)
- Shortness of breath, especially during exertion
- Wheezing or chest tightness
- Fatigue due to chronic respiratory difficulty
- Frequent respiratory infections or flare-ups
- Bluish lips or fingertips (cyanosis) in advanced cases
Causes
- Long-term exposure to tobacco smoke (primary cause)
- Air pollution or occupational exposure to dust and chemicals
- Repeated respiratory infections in childhood or adulthood
- Genetic predisposition (rare, e.g., alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency)
Risk Factors
- Smoking or exposure to secondhand smoke
- Living in areas with high air pollution
- Recurrent respiratory infections
- Age over 40 years
- Family history of chronic lung disease
- Occupational exposure to dust, fumes, or chemical irritants
Complications
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) progression
- Respiratory failure in advanced stages
- Frequent lung infections, pneumonia, or bronchiectasis
- Heart problems due to low oxygen levels (cor pulmonale)
- Reduced physical activity and quality of life
Prevention
- Avoid smoking and exposure to secondhand smoke
- Use protective equipment in dusty or chemical work environments
- Vaccinations against influenza and pneumonia
- Regular exercise and maintaining good respiratory health
- Prompt treatment of respiratory infections
Treatment Options in Korea
Treatment focuses on symptom management, slowing disease progression, and preventing complications:
- Medications:
- Bronchodilators (short-acting and long-acting) to open airways
- Inhaled corticosteroids to reduce inflammation
- Mucolytics to thin mucus and ease coughing
- Antibiotics during bacterial infections
- Therapies and interventions:
- Pulmonary rehabilitation programs for breathing exercises
- Oxygen therapy in advanced cases
- Lifestyle modification counseling, including smoking cessation
- Specialized hospitals in Korea:
- Samsung Medical Center Pulmonology Department
- Seoul National University Hospital Respiratory Clinic
- Asan Medical Center, Severance Hospital Pulmonology Units
- Multidisciplinary teams including pulmonologists, respiratory therapists, and nutritionists
- Follow-up care:
- Regular lung function tests (spirometry)
- Monitoring for infections and disease progression
- Patient education on inhaler use and symptom tracking