Overview
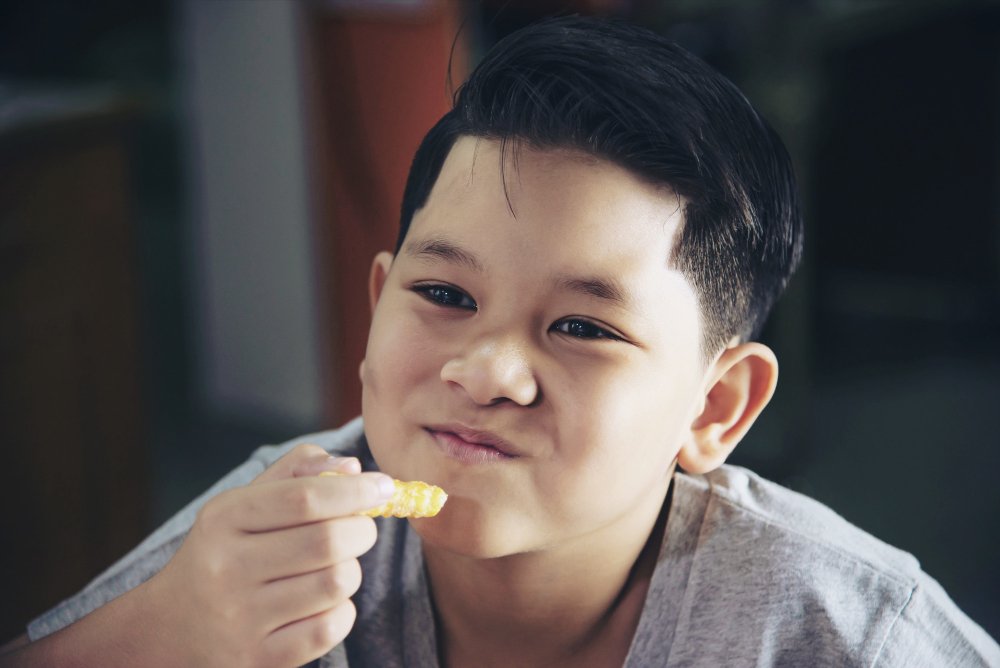
Childhood obesity is a medical condition where a child carries excess body fat that can negatively affect health. In Korea, rising rates of childhood obesity are a public health concern, associated with changes in diet, reduced physical activity, and sedentary lifestyles. Korean healthcare emphasizes early detection, lifestyle modification, and multidisciplinary management to prevent long-term complications.
What is Childhood Obesity?
Childhood obesity occurs when a child’s body mass index (BMI) is at or above the 95th percentile for children of the same age and sex. It increases the risk of developing metabolic, cardiovascular, and psychosocial complications both during childhood and later in adulthood.
Symptoms
- Excess body weight relative to height and age
- Increased waist circumference
- Fat accumulation around the abdomen, face, or limbs
- Low energy and reduced physical activity
- Early signs of puberty or hormonal changes in some children
- Social and emotional challenges, including low self-esteem
Causes
- Poor diet: High intake of sugary drinks, fast food, and processed snacks
- Sedentary lifestyle: Prolonged screen time, lack of physical exercise
- Genetic factors: Family history of obesity or metabolic disorders
- Medical conditions: Hypothyroidism, Cushing syndrome, Prader-Willi syndrome
- Environmental and socio-economic factors: Urban living, limited access to healthy foods, and lack of outdoor play areas
Risk Factors
- Overweight or obese parents
- Excessive consumption of calorie-dense foods
- Minimal daily physical activity
- Poor sleep patterns
- Early introduction of sugary foods
- Psychological stress or emotional eating
Complications
- Type 2 diabetes and insulin resistance
- Hypertension and dyslipidemia
- Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
- Sleep apnea and respiratory problems
- Orthopedic problems (e.g., joint pain)
- Psychological issues: low self-esteem, depression, and bullying
Prevention
- Encourage balanced, nutritious diets with fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins
- Limit sugary drinks and processed foods
- Promote daily physical activity (at least 60 minutes of moderate exercise)
- Reduce screen time (TV, smartphones, computers)
- Encourage healthy sleep habits
- Family-based lifestyle interventions and education
Treatment Options in Korea
Korean healthcare provides a multidisciplinary approach to manage childhood obesity effectively:
- Lifestyle modification programs:
- Personalized diet plans guided by pediatric nutritionists
- Structured physical activity and sports programs
- Behavioral therapy and family counseling
- Medical treatment:
- Medications may be considered for children with severe obesity or related comorbidities under strict medical supervision
- Close monitoring of growth, BMI, and metabolic parameters
- Specialized centers in Korea:
- Seoul National University Children’s Hospital, Samsung Medical Center, Asan Medical Center, Severance Hospital provide pediatric endocrinology and obesity clinics
- National health programs and school-based initiatives help prevent and monitor obesity
- Follow-up care:
- Regular assessments every 3–6 months for weight, BMI, and metabolic health
- Psychological support for children struggling with body image and social pressures