Overview
Chemical pneumonitis is a serious lung condition caused by inhalation or aspiration of chemical substances, such as industrial fumes, toxic gases, pesticides, cleaning agents, or gastric acid. It can lead to lung inflammation, breathing difficulties, and long-term respiratory problems if not treated promptly. In Korea, where industrial exposure and urban pollution are concerns, timely diagnosis and treatment of chemical pneumonitis are essential for preventing complications.
Symptoms
- Sudden shortness of breath
- Persistent cough (with or without mucus)
- Chest pain or tightness
- Wheezing or noisy breathing
- Fatigue and weakness
- Fever (if secondary infection occurs)
- Cyanosis (bluish skin or lips in severe cases)
Causes
Chemical pneumonitis occurs when harmful chemicals are inhaled or aspirated into the lungs. Common causes include:
- Inhalation of toxic industrial fumes or gases
- Aspiration of gastric acid (especially during vomiting or anesthesia)
- Exposure to pesticides, solvents, or chlorine-based cleaning agents
- Smoke inhalation from fires or explosions
- Accidental ingestion of corrosive substances leading to aspiration
Risk Factors
- Workers in chemical industries, mining, or agriculture
- Frequent exposure to strong cleaning agents or pesticides
- People with gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) (risk of aspiration)
- Elderly individuals or patients with swallowing difficulties
- Firefighters or individuals exposed to smoke inhalation
- Patients under anesthesia or unconscious state (higher aspiration risk)
Diagnosis
Doctors in Korea use a variety of diagnostic tools to confirm chemical pneumonitis, including:
- Medical history & exposure assessment (to identify the chemical source)
- Physical examination (lung sounds, oxygen levels)
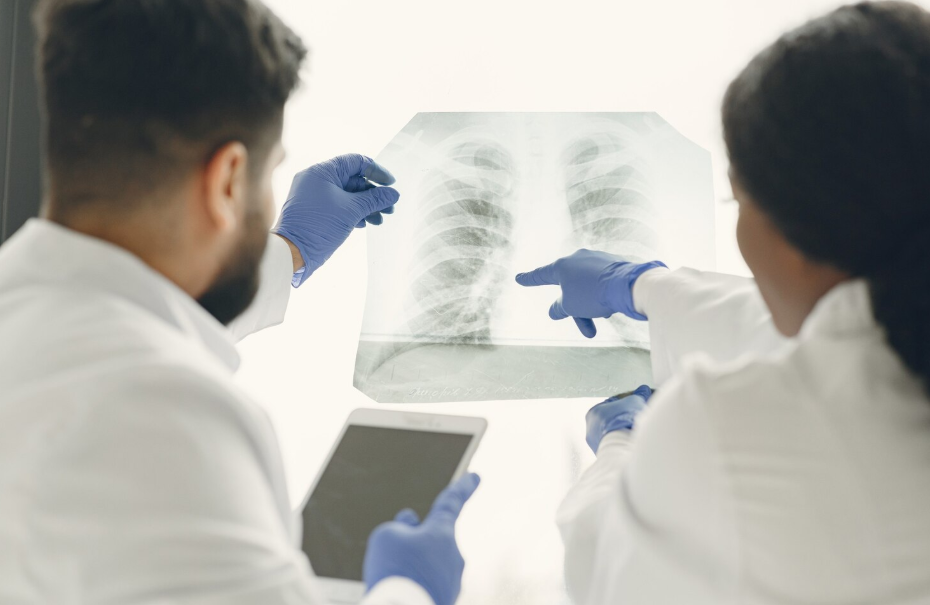
- Chest X-ray or CT scan (to detect inflammation or fluid in the lungs)
- Blood tests (oxygen levels, white blood cell count)
- Bronchoscopy (in some cases, to assess airway damage)
Prevention
- Use protective masks and proper ventilation in chemical industries
- Follow strict workplace safety regulations in Korea’s industrial settings
- Avoid exposure to strong household chemicals without protection
- Treat acid reflux or swallowing disorders to reduce aspiration risk
- Ensure proper handling and labeling of toxic substances
- Emergency training for chemical spills and inhalation accidents
Treatment Options in Korea
Treatment for chemical pneumonitis in Korea depends on the severity of lung injury:
- Immediate removal from exposure to the harmful chemical
- Hospitalization and oxygen therapy for breathing support
- Corticosteroids to reduce inflammation in severe cases
- Antibiotics if a secondary infection develops
- Bronchodilators to open airways and improve breathing
- Mechanical ventilation for severe respiratory failure
- Rehabilitation and respiratory therapy for long-term lung recovery
Korea’s advanced hospitals provide specialized respiratory care units equipped with high-tech ventilators, bronchoscopy, and rehabilitation services. Preventive education is also emphasized for workers in chemical industries to minimize future risks.