Overview
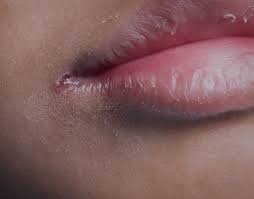
Cheilitis is the inflammation of the lips, which can cause redness, cracking, swelling, and discomfort. It may result from environmental factors, infections, allergies, or underlying medical conditions. In Korea, dermatology and oral medicine specialists provide accurate diagnosis and a range of treatment options to relieve symptoms and prevent recurrence.
Symptoms
- Red, dry, or cracked lips
- Swelling or tenderness of the lips
- Pain or burning sensation, especially when eating or speaking
- Scaling, flaking, or crust formation
- Itching or irritation
- Fissures at the corners of the mouth (angular cheilitis)
Causes
- Environmental factors such as sun exposure, wind, or cold weather
- Allergic reactions to lip products, toothpaste, or foods
- Infections: bacterial (e.g., Staphylococcus), fungal (e.g., Candida), or viral (e.g., herpes simplex)
- Nutritional deficiencies, especially vitamin B complex, iron, or zinc
- Chronic lip licking or biting
- Systemic conditions such as eczema or autoimmune disorders
Risk Factors
- Exposure to harsh environmental conditions
- Use of irritating cosmetics or lip products
- Poor oral hygiene
- Nutritional deficiencies
- Immune suppression or chronic illness
- Frequent lip licking or biting
Diagnosis
In Korea, cheilitis is diagnosed using:
- Physical examination of the lips and surrounding skin
- Patient history including exposure to irritants, habits, and underlying conditions
- Microbiological tests if infection is suspected
- Allergy testing for contact cheilitis
- Blood tests to detect nutritional deficiencies or systemic causes
Prevention
- Avoiding lip licking or biting
- Using protective lip balms with SPF
- Maintaining proper nutrition, including vitamins and minerals
- Avoiding allergens or irritants in cosmetics and oral care products
- Good oral hygiene and regular dental check-ups
- Moisturizing lips during dry or cold weather
Treatment Options in Korea
- Medical Management
- Topical antibiotics or antifungal creams for infections
- Topical corticosteroids for inflammatory or allergic cheilitis
- Antiviral medications for herpes-related cheilitis
- Nutritional supplements for deficiency-related cheilitis
- Lifestyle and Supportive Care
- Avoiding triggers such as irritants and allergens
- Using emollients and protective lip care products
- Hydration and proper diet
- Specialist Care
- Dermatologists or oral medicine specialists manage chronic or recurrent cases
- Patient education on prevention and early intervention