Overview
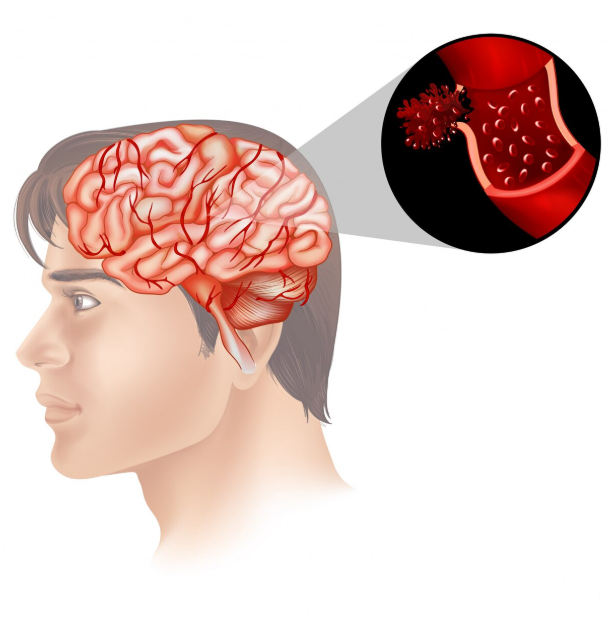
Cerebrovascular disease refers to a group of conditions that affect the blood vessels and blood flow in the brain, leading to events such as stroke, transient ischemic attacks (TIAs), and aneurysms. In Korea, advanced neurology and stroke centers provide rapid diagnosis, specialized treatment, and rehabilitation services, significantly improving patient outcomes.
Symptoms
- Sudden weakness or numbness, particularly on one side of the body
- Difficulty speaking or understanding speech
- Vision changes in one or both eyes
- Severe headache, sometimes with vomiting or confusion
- Dizziness, loss of balance, or coordination problems
- Facial drooping
- Confusion or difficulty concentrating
Causes
- Blockage of blood flow to the brain (ischemic stroke) due to a blood clot or atherosclerosis
- Rupture of a blood vessel (hemorrhagic stroke) from high blood pressure, aneurysm, or trauma
- Temporary reduction of blood flow causing transient ischemic attacks (TIAs)
- Cerebral aneurysms, arteriovenous malformations (AVMs), or other vascular malformations
Risk Factors
- Hypertension (high blood pressure)
- Diabetes mellitus
- High cholesterol levels
- Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption
- Obesity and sedentary lifestyle
- Age over 55 years
- Family history of stroke or cerebrovascular disease
- Heart disease or atrial fibrillation
Diagnosis
In Korea, cerebrovascular disease is diagnosed using:
- Neurological examination to assess strength, reflexes, and coordination
- Imaging studies: CT scan, MRI, MR angiography, or CT angiography
- Blood tests to evaluate cholesterol, blood sugar, and clotting factors
- Electrocardiogram (ECG) and echocardiography to detect heart-related causes
- Carotid ultrasound to assess blood flow in the neck arteries
Prevention
- Controlling blood pressure, diabetes, and cholesterol levels
- Maintaining a healthy diet and regular exercise
- Quitting smoking and limiting alcohol consumption
- Regular medical check-ups, especially for high-risk individuals
- Managing atrial fibrillation or other heart conditions
- Stress management and maintaining overall cardiovascular health
Treatment Options in Korea
- Acute Management
- Thrombolytic therapy (clot-busting drugs) for ischemic stroke
- Surgical interventions such as thrombectomy or aneurysm repair
- Blood pressure control and stabilization in hemorrhagic stroke
- Medical Management
- Antiplatelet medications (aspirin, clopidogrel)
- Anticoagulants for atrial fibrillation-related stroke prevention
- Lipid-lowering therapy (statins)
- Rehabilitation
- Physical therapy to restore strength and mobility
- Occupational therapy for daily activities
- Speech and language therapy for communication difficulties
- Psychological support and cognitive therapy
- Specialist Care
- Managed by neurologists and stroke specialists in Korean hospitals
- Multidisciplinary stroke units for monitoring and early intervention
- Long-term follow-up to prevent recurrence and manage complications