Overview
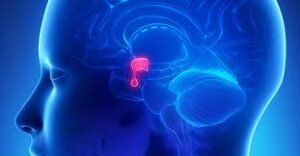
A cerebral aneurysm, also called a brain aneurysm, is a weakened or bulging area in the wall of a brain artery. It can remain asymptomatic, but if it ruptures, it may cause a life-threatening type of stroke called a subarachnoid hemorrhage. In Korea, advanced diagnostic imaging and minimally invasive neurosurgical techniques make early detection and treatment of cerebral aneurysms highly effective.
What is Cerebral Aneurysm?
A cerebral aneurysm occurs when a blood vessel in the brain develops a weak spot that balloons outward. While small aneurysms may not cause noticeable symptoms, large or ruptured aneurysms can result in severe neurological damage or death. Treatment in Korea focuses on preventing rupture through surgical or endovascular procedures.
Symptoms
Unruptured aneurysm:
- Headache (localized or persistent)
- Blurred or double vision
- Eye pain or drooping eyelid
- Weakness or numbness on one side of the face
Ruptured aneurysm:
- Sudden, severe headache (“thunderclap headache”)
- Nausea and vomiting
- Stiff neck
- Sensitivity to light (photophobia)
- Seizures
- Loss of consciousness
- Neurological deficits (speech, vision, weakness)
Causes
- Weakness in arterial walls (congenital or acquired)
- High blood pressure (hypertension)
- Atherosclerosis (hardening of arteries)
- Head trauma
- Infections affecting blood vessels
- Smoking and alcohol abuse
- Genetic conditions (polycystic kidney disease, connective tissue disorders)
Risk Factors
- Family history of cerebral aneurysm
- Age (commonly between 40–60 years)
- Female gender
- Hypertension
- Smoking and drug use (especially cocaine)
- Excessive alcohol consumption
- Certain inherited disorders (Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, Marfan syndrome)
Complications
- Subarachnoid hemorrhage (life-threatening brain bleed)
- Hydrocephalus (fluid buildup in the brain)
- Vasospasm (narrowing of brain arteries after bleeding)
- Permanent brain damage
- Stroke
- Death in severe ruptures
Prevention
- Controlling blood pressure through lifestyle and medication
- Avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol use
- Regular brain imaging if there is a family history of aneurysm
- Managing cholesterol and vascular health
- Early treatment of small aneurysms before rupture
Treatment Options in Korea
Korean neurosurgery centers are globally recognized for high success rates in aneurysm treatment using state-of-the-art imaging and surgical methods.
Diagnosis
- CT angiography (CTA)
- MRI/MRA (Magnetic Resonance Angiography)
- Digital Subtraction Angiography (DSA) – gold standard
Treatment Approaches
- Endovascular coiling – A minimally invasive procedure where coils are inserted to block blood flow into the aneurysm (commonly performed in Korea).
- Surgical clipping – Open brain surgery to place a clip at the base of the aneurysm to prevent rupture.
- Flow-diverting stents – For large or complex aneurysms, redirecting blood flow away from the aneurysm sac.
- Neuro-intensive care – For managing ruptured aneurysms with monitoring and rehabilitation.
Rehabilitation and Support
- Physical and occupational therapy for stroke recovery
- Speech therapy for communication issues
- Long-term follow-up with brain imaging