Overview
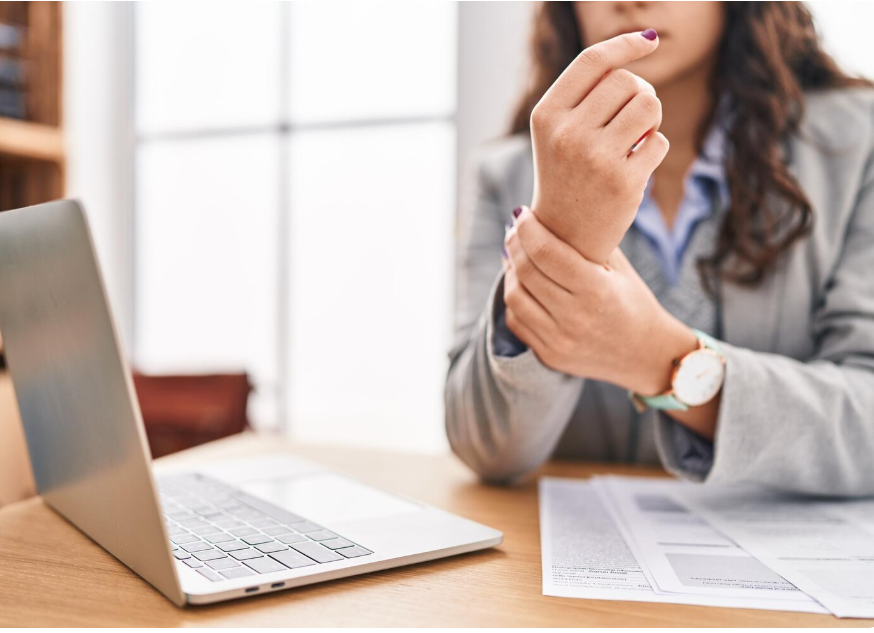
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS) is a condition caused by compression of the median nerve as it passes through the carpal tunnel in the wrist. It leads to pain, numbness, and weakness in the hand and fingers. In Korea, advanced orthopedic and neurology centers provide diagnostic testing, conservative management, and surgical treatment to relieve symptoms and restore hand function.
Symptoms
- Numbness or tingling in the thumb, index, middle, and half of the ring finger
- Hand or wrist pain, sometimes radiating up the arm
- Weakness or clumsiness in the hand, affecting grip
- Burning or itching sensations in fingers
- Symptoms often worsen at night or during repetitive hand activities
Causes
- Repetitive hand movements (typing, assembly line work, using tools)
- Wrist injuries or fractures
- Conditions such as diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, or thyroid disorders
- Fluid retention during pregnancy or menopause
- Anatomical variations narrowing the carpal tunnel
Risk Factors
- Occupations involving repetitive hand or wrist motion
- Female gender (higher incidence due to smaller carpal tunnel)
- Age above 40
- Diabetes or metabolic disorders
- Pregnancy, obesity, or hormonal changes
- Previous wrist injuries
Diagnosis
In Korea, CTS is diagnosed using:
- Physical examination including Tinel’s sign and Phalen’s test
- Electrodiagnostic studies (nerve conduction studies and electromyography)
- Ultrasound to assess median nerve swelling
- MRI in rare cases to detect anatomical abnormalities
- Patient history of symptom onset and occupational exposure
Prevention
- Ergonomic adjustments in the workplace
- Regular breaks during repetitive hand tasks
- Wrist stretches and exercises
- Maintaining proper posture and hand positioning
- Early evaluation of wrist pain or numbness
Treatment Options in Korea
- Non-Surgical Management
- Wrist splints, especially at night
- Anti-inflammatory medications (NSAIDs)
- Corticosteroid injections for severe inflammation
- Physical therapy and nerve gliding exercises
- Surgical Treatment
- Carpal tunnel release surgery to relieve pressure on the median nerve
- Open or endoscopic techniques available in advanced Korean hospitals
- Outpatient procedure with rapid recovery for most patients
- Post-Treatment Care
- Rehabilitation exercises to restore strength and flexibility
- Regular follow-up to monitor symptom resolution
- Patient education on activity modification to prevent recurrence