Overview
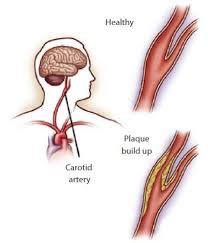
Carotid Artery Disease occurs when the carotid arteries, the major blood vessels supplying the brain, become narrowed or blocked due to atherosclerosis. This increases the risk of stroke or transient ischemic attacks (TIAs). In Korea, advanced cardiology and vascular surgery centers provide early detection, imaging, and both medical and surgical treatments to prevent complications.
Symptoms
- Often asymptomatic in early stages
- Sudden weakness or numbness in the face, arms, or legs
- Difficulty speaking or understanding speech (aphasia)
- Sudden vision problems in one eye
- Dizziness or loss of balance
- Transient ischemic attacks (“mini-strokes”) may precede major stroke
Causes
- Atherosclerosis: buildup of plaque in the carotid arteries
- High blood pressure
- High cholesterol and lipid disorders
- Smoking and tobacco use
- Diabetes
- Rarely, arterial dissection or inflammation
Risk Factors
- Age above 50
- Hypertension and high cholesterol
- Smoking and excessive alcohol use
- Diabetes or metabolic syndrome
- Family history of stroke or heart disease
- Obesity and sedentary lifestyle
Diagnosis
In Korea, carotid artery disease is diagnosed through:
- Physical examination to detect bruits (abnormal artery sounds)
- Doppler ultrasound to assess blood flow and plaque buildup
- CT angiography or MR angiography for detailed imaging
- Carotid angiography in specialized centers for precise evaluation
- Blood tests to monitor cholesterol, blood sugar, and inflammatory markers
Prevention
- Maintaining healthy blood pressure and cholesterol levels
- Smoking cessation and limiting alcohol intake
- Regular physical activity and weight management
- Healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains
- Managing diabetes and other chronic conditions
- Routine screening for at-risk individuals
Treatment Options in Korea
- Medical Management
- Antiplatelet therapy (aspirin, clopidogrel) to prevent clots
- Cholesterol-lowering medications (statins)
- Blood pressure control
- Lifestyle modification and rehabilitation programs
- Surgical and Interventional Treatments
- Carotid endarterectomy: surgical removal of plaque
- Carotid artery stenting: minimally invasive procedure to open narrowed arteries
- Performed in advanced hospitals such as Seoul National University Hospital, Asan Medical Center, and Samsung Medical Center
- Follow-Up Care
- Regular imaging and check-ups to monitor artery health
- Ongoing medication and lifestyle adjustments
- Rehabilitation for patients who experienced TIAs or stroke