Overview
Bronchiolitis is a common respiratory infection primarily affecting infants and young children, characterized by inflammation and congestion in the small airways (bronchioles) of the lungs. This condition often leads to coughing, wheezing, difficulty breathing, and in severe cases, hospitalization.
In Korea, bronchiolitis is managed in pediatric and respiratory clinics, where specialized care ensures early diagnosis, symptom management, and supportive treatment. Korean hospitals emphasize preventing complications and providing guidance to parents for home care while utilizing modern diagnostic tools and treatment approaches.
What is Bronchiolitis?
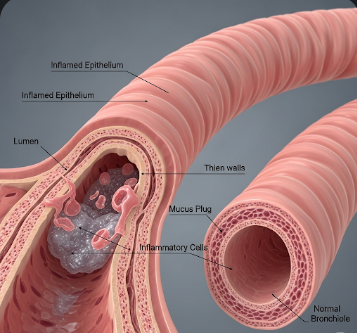
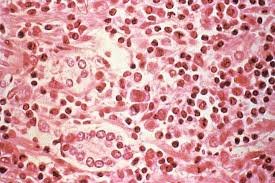
Bronchiolitis is an inflammation of the bronchioles, the tiny air passages in the lungs. The inflammation is usually caused by a viral infection, most commonly Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV). The swelling and mucus production in the bronchioles narrow the airways, leading to difficulty in air exchange, wheezing, and labored breathing.
Bronchiolitis is typically self-limiting in mild cases but can become severe in infants, premature babies, or children with underlying health conditions.
Symptoms
The symptoms of bronchiolitis usually develop gradually and may include:
- Runny nose and nasal congestion
- Mild fever
- Cough
- Wheezing or high-pitched breathing sounds
- Rapid or labored breathing
- Retractions (pulling in of the chest muscles during breathing)
- Fatigue or irritability
- Poor feeding in infants
- Bluish color of lips or face in severe cases
Symptoms often peak 3–5 days after onset and typically last 1–2 weeks, although cough may persist longer.
Causes
The main cause of bronchiolitis is a viral infection, with the most common viruses being:
- Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) – the most frequent cause
- Rhinovirus
- Influenza virus
- Parainfluenza virus
- Adenovirus
These viruses are spread via respiratory droplets, direct contact with contaminated surfaces, or close contact with infected individuals.
Risk Factors
Certain children are at higher risk for severe bronchiolitis:
- Infants under 12 months, especially under 6 months
- Premature babies with underdeveloped lungs
- Children with chronic lung diseases (e.g., bronchopulmonary dysplasia)
- Children with congenital heart disease
- Immunocompromised children
- Exposure to tobacco smoke
- Crowded living conditions or daycare attendance
Complications
While most cases of bronchiolitis are mild, complications can occur:
- Severe respiratory distress requiring hospitalization
- Dehydration due to difficulty feeding
- Hypoxemia (low blood oxygen levels)
- Secondary bacterial infections, such as pneumonia or ear infections
- Exacerbation of underlying chronic lung or heart conditions
- Rarely, respiratory failure requiring intensive care
Prevention
Preventive measures focus on reducing viral exposure and supporting infant health:
- Frequent hand washing for caregivers and family members
- Avoiding contact with sick individuals, especially during peak viral season
- Disinfecting surfaces and toys
- Limiting exposure to crowded places for infants during RSV season
- Breastfeeding to enhance immunity
- Palivizumab injections (monoclonal antibody) for high-risk infants to prevent RSV infection
- Maintaining good indoor air quality and avoiding tobacco smoke
Treatment Options in Korea
Diagnosis
Diagnosis involves a combination of clinical evaluation and supportive tests:
- Medical history and symptom assessment
- Physical examination, including lung auscultation for wheezing or crackles
- Pulse oximetry to monitor oxygen levels
- Chest X-rays in severe cases to rule out pneumonia or other complications
- Viral testing is occasionally performed to identify the causative agent
Medical Management
Treatment is primarily supportive, as bronchiolitis is usually viral:
- Oxygen therapy for children with low oxygen levels
- Hydration support, including IV fluids in severe cases
- Nasal suctioning to clear mucus and improve breathing
- Fever management with acetaminophen or ibuprofen
- Monitoring in hospital for infants at risk of complications
Medications:
- Bronchodilators may be used in selected cases, although routine use is not universally recommended
- Antivirals are rarely required, except in specific high-risk patients
- Antibiotics are only prescribed if a secondary bacterial infection develops
Supportive Care at Home
For mild cases managed at home:
- Frequent small feedings to maintain nutrition
- Humidified air to ease breathing
- Keeping the child upright to improve airway drainage
- Monitoring breathing patterns and seeking immediate care for distress or cyanosis
Prognosis
The prognosis for bronchiolitis is generally favorable, particularly with early recognition and supportive care:
- Most children recover within 1–2 weeks
- Hospitalization is required for severe cases but outcomes are excellent with appropriate care
- Long-term complications are rare, though some children may develop wheezing or asthma-like symptoms later
- Korean pediatric care emphasizes early intervention, monitoring, and parent education, ensuring that infants receive timely treatment and guidance to minimize risks
With specialized pediatric care, advanced monitoring, and comprehensive parent guidance, Korea provides safe and effective management for bronchiolitis, ensuring infants recover fully while reducing the risk of complications and long-term respiratory issues.