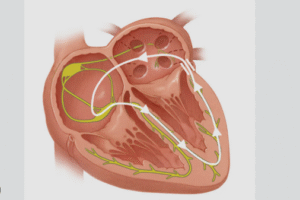
Overview
Bradycardia is a medical condition characterized by an abnormally slow heart rate, usually defined as fewer than 60 beats per minute in adults. While some individuals, particularly athletes, may have a naturally low heart rate without symptoms, bradycardia can also indicate an underlying heart condition or systemic problem requiring medical evaluation.
In Korea, bradycardia is managed in cardiology and internal medicine clinics, where specialists use advanced diagnostic tools, cardiac monitoring, and treatment interventions such as pacemaker implantation when necessary. Korean hospitals provide comprehensive care for bradycardia, ranging from lifestyle adjustments to surgical solutions, ensuring patient safety and long-term heart health.
What is Bradycardia?
Bradycardia occurs when the electrical impulses that regulate the heartbeat are slowed or blocked. This condition can involve:
- Sinus bradycardia: The heart’s natural pacemaker, the sinoatrial (SA) node, generates impulses too slowly
- Heart block: Impaired transmission of electrical signals between the atria and ventricles
- Junctional or ventricular bradycardia: Less common forms arising from secondary pacemakers in the heart
Depending on the type and severity, bradycardia can range from asymptomatic to life-threatening, especially if it impairs blood flow to vital organs.
Symptoms
Symptoms vary depending on heart rate, underlying cause, and overall cardiovascular health:
- Fatigue or weakness due to reduced cardiac output
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Fainting (syncope) or near-fainting episodes
- Shortness of breath, particularly during exertion
- Chest discomfort or palpitations
- Confusion or memory problems in older adults
- Exercise intolerance and decreased stamina
Many people with mild bradycardia may remain asymptomatic and only discover the condition during routine health check-ups or electrocardiograms (ECGs).
Causes
Bradycardia can result from a variety of cardiac and non-cardiac factors:
Cardiac causes:
- Degeneration of the heart’s electrical system with age
- Ischemic heart disease or myocardial infarction
- Congenital heart defects affecting electrical pathways
- Heart valve disorders
Non-cardiac causes:
- Hypothyroidism or other endocrine disorders
- Electrolyte imbalances, especially high potassium
- Certain medications such as beta-blockers, calcium channel blockers, or antiarrhythmic drugs
- Sleep apnea and severe hypothermia
- Inflammatory conditions affecting the heart (myocarditis)
Lifestyle factors:
- High levels of physical fitness leading to naturally lower resting heart rates
- Excessive use of recreational drugs or alcohol in some cases
Risk Factors
- Advanced age: Age-related degeneration of cardiac conduction system
- Underlying heart disease: Previous heart attacks or structural abnormalities
- Use of certain medications: Beta-blockers, digoxin, and antiarrhythmic drugs
- Chronic conditions: Hypothyroidism, diabetes, or chronic kidney disease
- Family history of bradyarrhythmias or sudden cardiac death
- Sleep disorders: Sleep apnea increases risk of nocturnal bradycardia
Complications
If untreated, bradycardia can lead to serious cardiovascular and systemic complications:
- Heart failure due to insufficient blood supply
- Frequent fainting or falls, increasing risk of injury
- Reduced organ perfusion, potentially affecting kidneys, brain, and liver
- Sudden cardiac arrest in severe cases
- Development of arrhythmias like atrial fibrillation or ventricular tachycardia
- Reduced quality of life due to fatigue and exercise intolerance
Prevention
While some forms of bradycardia cannot be prevented, steps to reduce risk and maintain heart health include:
- Regular cardiovascular check-ups, especially for older adults
- Managing underlying conditions such as hypertension, diabetes, and thyroid disorders
- Avoiding medications or substances that slow heart rate unless prescribed
- Monitoring fitness routines to prevent excessive bradycardia in athletes
- Early evaluation of symptoms such as dizziness, syncope, or fatigue
- Lifestyle modifications: Balanced diet, regular exercise, and avoiding tobacco and excessive alcohol
Treatment Options in Korea
Diagnosis
Accurate diagnosis is critical to determine type, severity, and underlying cause:
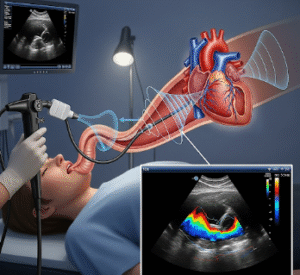
- Electrocardiogram (ECG): Measures electrical activity and identifies slow heart rates
- Holter monitor: Continuous 24–48 hour monitoring for intermittent bradycardia
- Event recorder or implantable loop recorder: For occasional or asymptomatic episodes
- Blood tests: Assess thyroid function, electrolytes, and cardiac biomarkers
- Echocardiography: Evaluates heart structure and function
- Stress tests: Determine heart response to physical exertion
Medical Management
- Adjusting medications: Reducing or discontinuing drugs that slow heart rate
- Treatment of underlying conditions: Managing hypothyroidism, electrolyte imbalance, or sleep apnea
- Temporary pacing: In acute symptomatic cases in hospital settings
Surgical Management
- Pacemaker implantation: Permanent solution for severe or symptomatic bradycardia
- Single-chamber pacemakers for isolated ventricular bradycardia
- Dual-chamber pacemakers for coordination between atria and ventricles
- Rate-responsive pacemakers adjusting heart rate according to activity
Supportive Care
- Lifestyle modification: Exercise moderation, healthy diet, stress management
- Regular follow-ups: Routine device checks for pacemaker patients
- Patient education: Recognizing symptoms of worsening bradycardia and when to seek immediate care
Prognosis
The prognosis for bradycardia depends on cause, severity, and timely treatment:
- Asymptomatic or mild bradycardia: Often benign with minimal impact on daily life
- Underlying heart disease-related bradycardia: Requires close monitoring and treatment
- Severe symptomatic bradycardia: Pacemaker implantation dramatically improves quality of life and reduces risk of complications
- Korean hospitals provide state-of-the-art cardiology care, including advanced pacemaker implantation and cardiac monitoring, ensuring effective long-term management
- Early detection and comprehensive treatment lead to excellent outcomes and prevention of serious cardiovascular events
With advanced diagnostic capabilities, cardiac expertise, and patient-centered care, Korea offers optimal management for bradycardia, ensuring patients maintain healthy heart function and quality of life.