Overview
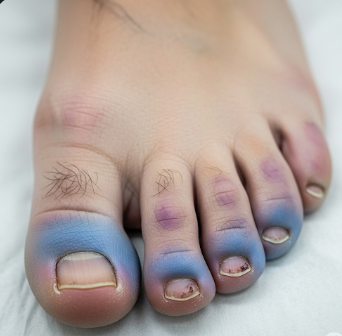
Blue Toe Syndrome (BTS) is a vascular condition characterized by painful, discolored toes due to impaired blood flow, often caused by small arterial blockages or emboli. The toes appear blue, purple, or dark red, reflecting reduced oxygenation of the tissues. Although the condition primarily affects the feet, it may signal serious underlying vascular disease, including cholesterol emboli, peripheral arterial disease, or thromboembolic events.
In Korea, Blue Toe Syndrome is diagnosed promptly in specialized vascular clinics, where cardiologists, vascular surgeons, and interventional radiologists collaborate for treatment. Early recognition is critical to prevent tissue loss, gangrene, or systemic complications. Korean hospitals also emphasize preventive vascular health measures, particularly in high-risk patients.
What is Blue Toe Syndrome?
Blue Toe Syndrome refers to discoloration of one or more toes caused by reduced arterial blood flow, typically without obvious trauma. It often occurs suddenly and can affect both elderly and middle-aged adults.
Key characteristics:
- Painful, blue or purple toes
- Cold sensation in affected toes
- Possible ulceration or necrosis in severe cases
- Often associated with cholesterol crystal embolization (atheroembolism) or small arterial thrombi
BTS is usually a sign of systemic vascular issues, making early investigation of the circulatory system essential.
Symptoms
The presentation varies with severity and cause:
- Bluish, purple, or dark-red discoloration of one or multiple toes
- Pain or tenderness in affected toes
- Cold or numb sensation
- Swelling in some cases
- Ulcer formation or tissue necrosis in severe, untreated cases
- Delayed capillary refill when the toe is pressed
- Possible associated skin changes such as mottling or gangrene
Symptoms often develop suddenly, particularly in cases related to embolic events, requiring prompt medical evaluation.
Causes
Blue Toe Syndrome arises from impaired blood flow or embolic events in the small arteries of the toes.
Common causes include:
- Cholesterol emboli: Dislodged plaques from larger arteries (common in atherosclerosis)
- Thromboembolism: Blood clots from the heart or major arteries
- Peripheral arterial disease: Narrowed arteries reduce blood flow
- Vasospasm: Sudden narrowing of small arteries due to Raynaud’s phenomenon or cold exposure
- Trauma: Rarely, injury or frostbite may lead to localized BTS
- Medical procedures: Vascular surgery, angiography, or anticoagulant therapy may trigger emboli
Risk factors like hypertension, diabetes, smoking, and hyperlipidemia increase the likelihood of BTS.
Risk Factors
- Atherosclerosis: Plaque buildup in large arteries
- Heart conditions: Atrial fibrillation, endocarditis, or cardiac thrombi
- Kidney disease: Especially in patients on hemodialysis
- Diabetes: Microvascular complications increase susceptibility
- High cholesterol or hyperlipidemia
- Smoking and lifestyle factors
- Older age: Vascular changes are more common in elderly adults
- Recent vascular interventions: Angioplasty, stent placement, or vascular surgery
Complications
If untreated, Blue Toe Syndrome may lead to serious complications:
- Gangrene: Tissue death requiring amputation in severe cases
- Infection: Secondary infections from ulcers or necrotic tissue
- Chronic pain: Persistent discomfort in affected toes
- Progressive vascular disease: Indicates risk of systemic embolism or cardiovascular events
- Functional impairment: Difficulty walking or performing daily activities
- Organ complications: Emboli may also affect kidneys, brain, or other organs
Prevention
Preventive strategies in Korea focus on vascular health, lifestyle modification, and early detection:
- Control of cardiovascular risk factors: Blood pressure, cholesterol, and blood sugar management
- Regular vascular check-ups: Screening for peripheral arterial disease and atherosclerosis
- Healthy lifestyle: Balanced diet, exercise, smoking cessation, and weight management
- Medications: Antiplatelets, anticoagulants, or statins for at-risk patients
- Avoid cold exposure or trauma: Protect toes to prevent vasospasm or injury
- Prompt treatment of underlying heart or vascular conditions
Treatment Options in Korea
Diagnosis
Korean medical centers utilize advanced diagnostic techniques to identify BTS causes:
- Physical examination: Assess discoloration, temperature, and capillary refill
- Doppler ultrasound: Detect arterial blood flow and blockages
- Angiography: Visualize small and large arteries for emboli or stenosis
- Blood tests: Evaluate cholesterol, coagulation, and kidney function
- Echocardiography: Check for cardiac sources of emboli
- CT or MRI angiography: For detailed vascular imaging
Medical Management
- Anticoagulation therapy: Prevents new clots or emboli
- Antiplatelet therapy: Reduces risk of arterial blockage
- Pain management: Analgesics for discomfort
- Treatment of underlying conditions: Diabetes, hypertension, or hyperlipidemia
Interventional and Surgical Management
- Embolectomy: Removal of arterial emboli in severe cases
- Endovascular interventions: Angioplasty or stent placement to restore blood flow
- Surgical bypass: In cases of extensive peripheral arterial disease
- Debridement or amputation: For necrotic or gangrenous toes
Supportive Care
- Wound care for ulcers or necrotic tissue
- Physical therapy to maintain mobility and prevent secondary complications
- Lifestyle guidance and vascular risk management
- Education on early signs of worsening ischemia or embolic events
Prognosis
The prognosis for Blue Toe Syndrome in Korea depends on early detection, severity, and management of underlying vascular disease:
- Mild cases with prompt medical treatment may fully recover without lasting effects
- Severe cases with gangrene or necrosis may require surgical intervention, including partial amputation
- Managing underlying cardiovascular risk factors improves long-term outcomes
- With modern diagnostic and interventional care available in Korean hospitals, patients can achieve significant improvement, prevent tissue loss, and reduce recurrence risk