Overview
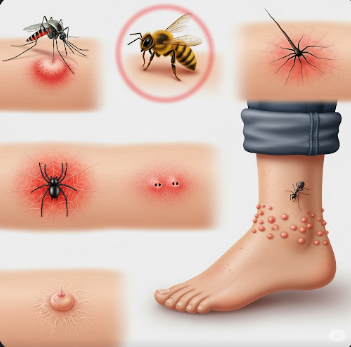
Bites and stings occur when humans come into contact with insects, arachnids, snakes, or other animals, leading to local or systemic reactions. While most bites and stings are minor and cause temporary discomfort, some can result in allergic reactions, infections, or severe medical complications.
In Korea, medical facilities provide immediate treatment for bites and stings, including emergency care for allergic reactions, anti-venom administration, wound management, and infection prevention. Awareness and prevention strategies are emphasized, especially during outdoor activities.
What are Bites and Stings?
- Bites occur when an animal or insect penetrates the skin with teeth or mandibles, potentially introducing bacteria, viruses, or venom. Common examples include dog bites, cat bites, and spider bites.
- Stings occur when an insect injects venom using a stinger, as seen in bees, wasps, hornets, and certain marine animals.
The body may respond with local inflammation, pain, swelling, redness, and itching, while severe reactions can affect multiple organ systems.
Symptoms
Symptoms depend on the type of bite or sting and individual sensitivity:
Local reactions:
- Pain, redness, and swelling at the site
- Warmth or tenderness
- Itching or hives
- Blistering or bruising
Systemic reactions:
- Nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea
- Fever or chills from infection
- Dizziness, fainting, or rapid heartbeat
- Shortness of breath or wheezing (allergic reaction)
- Anaphylaxis in severe allergic responses, which can be life-threatening
Causes
Bites and stings occur when humans encounter animals or insects, either accidentally or provocatively. Common causes in Korea include:
- Insect bites: Mosquitoes, ticks, fleas, ants, bees, wasps
- Arachnid bites: Spiders or scorpions
- Animal bites: Dogs, cats, or wild animals
- Marine stings: Jellyfish or sea urchins in coastal areas
- Environmental exposure: Hiking, camping, or outdoor work increases risk
Risk Factors
- Outdoor activities such as hiking, camping, or gardening
- Exposure to areas with high insect populations or wildlife
- Lack of protective clothing or insect repellents
- Previous allergic reactions to insect stings or animal bites
- Immune system deficiencies or chronic medical conditions
Complications
Complications can arise from bites and stings if untreated or in sensitive individuals:
- Infections: Bacterial infections like cellulitis, abscesses, or tetanus
- Allergic reactions: Ranging from mild itching to life-threatening anaphylaxis
- Venom-related complications: Tissue damage, necrosis, or organ dysfunction in venomous bites
- Secondary complications: Scarring, chronic pain, or joint involvement in severe injuries
Prevention
Preventive measures are key to reducing the risk of bites and stings:
- Avoidance: Stay away from areas with high insect or animal activity
- Protective clothing: Long sleeves, pants, and gloves during outdoor activities
- Insect repellents: DEET or natural alternatives for exposed skin
- Proper footwear: To prevent snake, insect, or scorpion bites
- Animal safety: Avoid interacting with stray or unfamiliar animals
- Vaccinations: Ensure tetanus vaccination is up to date
- Awareness: Educate children and adults about safe behaviors around animals and insects
Treatment Options in Korea
First Aid and Immediate Care
- Cleaning the wound: Wash bite or sting site with soap and water to reduce infection risk
- Cold compress: Apply ice packs to reduce swelling and pain
- Elevation: Keep affected limb elevated to minimize swelling
- Topical treatments: Apply antiseptics or hydrocortisone cream for itching and inflammation
Medical Management
- Pain relief: Over-the-counter analgesics such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen
- Antihistamines: For mild to moderate allergic reactions
- Antibiotics: Prescribed if infection develops, especially in animal bites
- Tetanus booster: Administered if vaccination is not up to date
- Emergency care: For anaphylaxis, epinephrine injection (EpiPen) is life-saving
Venomous Bites and Stings
- Anti-venom therapy: Available for snake bites or severe insect envenomation
- Supportive care: Monitoring vital signs and treating organ dysfunction if necessary
- Hospitalization: Required for severe systemic reactions or complications
Rehabilitation and Follow-Up
- Wound care and monitoring for signs of infection
- Physical therapy if joint or nerve injury occurs
- Allergy testing for individuals with repeated reactions
- Education on future prevention strategies
Prognosis
Most bites and stings in Korea result in mild, self-limiting symptoms when treated promptly. With proper first aid, medical care, and monitoring, recovery is generally complete within days to weeks. Severe allergic reactions or venomous bites require immediate medical attention, but with timely intervention, long-term complications are rare. Public health initiatives and access to modern healthcare have greatly improved the outcomes for individuals affected by bites and stings in Korea.