Overview
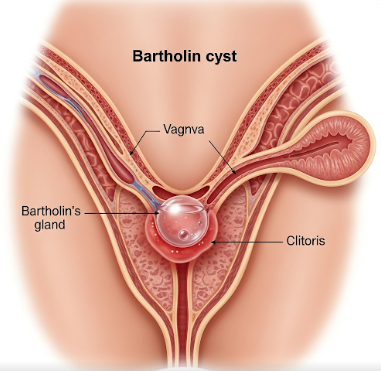
A Bartholin cyst is a fluid-filled swelling that develops in one of the Bartholin glands, located on each side of the vaginal opening. These glands are responsible for secreting fluid that helps lubricate the vagina. Bartholin cysts are relatively common in women, particularly during reproductive years, and while many cysts are painless, they can occasionally become infected, leading to Bartholin gland abscesses that cause pain, redness, and swelling.
In Korea, gynecology clinics and hospitals provide comprehensive evaluation and treatment for Bartholin cysts. Advanced diagnostic tools, minimally invasive procedures, and post-treatment care ensure rapid recovery and minimize the risk of recurrence. Awareness, early management, and proper hygiene are essential for preventing complications.
What is a Bartholin Cyst?
A Bartholin cyst forms when the duct of a Bartholin gland becomes blocked, preventing the normal flow of fluid. This blockage causes fluid to accumulate, creating a soft, painless lump at the vaginal opening. If bacteria enter the cyst, an abscess may develop, resulting in pain, inflammation, and sometimes fever.
Bartholin cysts vary in size, ranging from very small and asymptomatic to large, noticeable swellings that can interfere with walking, sitting, or sexual activity. While benign, timely treatment is important to prevent infection, discomfort, or repeated cyst formation.
Symptoms
Symptoms of a Bartholin cyst can vary depending on size and whether infection is present:
- Small, painless lump near the vaginal opening
- Swelling on one side of the vulva
- Discomfort or pain during walking, sitting, or sexual activity
- Redness or tenderness if infection occurs
- Fever or malaise in the case of an abscess
- Difficulty in hygiene maintenance due to the swelling
Many small Bartholin cysts are discovered incidentally and may not cause noticeable symptoms until they enlarge or become infected.
Causes
Bartholin cysts occur primarily due to blockage of the gland’s duct, which can result from:
- Infections: Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) like gonorrhea or chlamydia can contribute to duct blockage.
- Trauma or irritation: Minor injuries, friction, or sexual activity can cause swelling that blocks the duct.
- Inflammation: Chronic inflammation of the vulvar tissue may lead to cyst formation.
- Age and hormonal changes: Women of reproductive age are more susceptible, while postmenopausal women are less commonly affected.
The cyst itself is not caused directly by sexual activity, but infections that block the duct may be sexually transmitted.
Risk Factors
Certain factors increase the likelihood of developing a Bartholin cyst:
- Age: Most common in women aged 20–30 years.
- History of cysts: Prior occurrence increases the risk of recurrence.
- Sexually transmitted infections: History of STIs may contribute.
- Poor hygiene: Increases susceptibility to infection-related blockage.
- Chronic inflammation: Conditions affecting vulvar tissue may elevate risk.
Complications
While most Bartholin cysts are benign and easily treated, complications can occur:
- Bartholin gland abscess: Infection of the cyst, causing severe pain, redness, and fever.
- Recurrent cysts: Some women experience repeated cyst formation, requiring repeated treatment.
- Sexual discomfort: Large or infected cysts can make sexual activity painful.
- Rare malignancy: In postmenopausal women, unusual cysts may rarely harbor cancer, making evaluation essential.
Prompt medical attention and appropriate treatment help prevent these complications.
Prevention
Preventing Bartholin cysts focuses on maintaining hygiene, reducing infections, and monitoring symptoms:
- Practice safe sex: Use condoms to reduce the risk of STIs that can cause cyst formation.
- Maintain vulvar hygiene: Regular cleansing with mild soap and water.
- Seek early treatment for infections: Prompt management of STIs or vulvar infections reduces risk.
- Monitor for symptoms: Early detection of lumps can prevent infection and abscess formation.
- Avoid unnecessary trauma: Gentle care during sexual activity and hygiene practices.
Korean gynecology clinics provide education on preventive measures and sexual health counseling to reduce recurrence risk.
Treatment Options in Korea
Treatment for Bartholin cysts in Korea is individualized, depending on cyst size, symptoms, and infection status:
1. Diagnosis:
- Physical examination: Identification of cyst location, size, and signs of infection.
- Ultrasound: Imaging for large or recurrent cysts to rule out other vulvar masses.
- Laboratory tests: If infection is suspected, swabs may be taken to identify bacterial or sexually transmitted pathogens.
2. Medical Treatments:
- Sitz baths: Warm water baths several times a day help reduce discomfort and promote drainage in small, non-infected cysts.
- Pain relief: Analgesics and anti-inflammatory medications for discomfort.
- Antibiotics: Prescribed if the cyst is infected or an abscess forms.
3. Surgical and Minimally Invasive Procedures:
- Incision and drainage: Immediate relief for abscesses, often followed by catheter placement to allow continuous drainage.
- Marsupialization: A minor surgical procedure to create a permanent opening for drainage and reduce recurrence risk.
- Excision: Complete removal of the Bartholin gland in cases of repeated cyst formation or in postmenopausal women.
4. Follow-up and Support:
- Post-treatment monitoring: Ensures proper healing and absence of infection.
- Lifestyle and hygiene counseling: Guidance on preventing recurrence and promoting vulvar health.
- Sexual health support: For women experiencing discomfort during sexual activity due to cysts.
Korean hospitals are recognized for their expertise in minimally invasive procedures, offering rapid recovery, low recurrence rates, and comprehensive patient support.
In conclusion, a Bartholin cyst is a common and often manageable condition affecting women of reproductive age. Early detection, proper hygiene, infection control, and specialized treatment are key to preventing complications and recurrence. Korea’s modern gynecological care ensures patients receive expert diagnosis, effective treatment, and guidance for long-term vulvar health, allowing a safe and comfortable recovery.