Overview
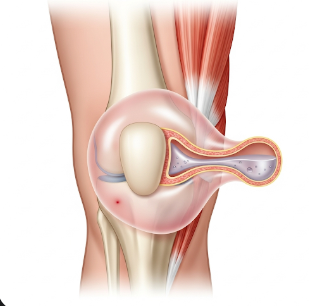
A Baker’s cyst, also known as a popliteal cyst, is a fluid-filled swelling that develops behind the knee. It occurs when excess synovial fluid from the knee joint or surrounding structures accumulates, forming a bulge that can cause discomfort, stiffness, and restricted movement. While Baker’s cysts are often associated with underlying knee conditions such as arthritis or meniscus injuries, they can sometimes occur without an obvious cause. In Korea, orthopedic and sports medicine specialists provide advanced diagnostic techniques and minimally invasive treatment options for Baker’s cysts. Hospitals and clinics focus not only on relieving symptoms but also on addressing the root causes, ensuring long-term knee health and mobility.
What is a Baker’s Cyst?
A Baker’s cyst is a benign swelling that forms in the popliteal space, the area behind the knee joint. It results from the buildup of synovial fluid, which lubricates and nourishes the knee. This fluid may leak out of the joint due to inflammation or injury, collecting in a sac behind the knee. Baker’s cysts are common in adults, especially those with osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, or meniscus tears, but they can also occur in children. While many cysts are small and asymptomatic, larger cysts can cause pain, tightness, and even affect walking.
Symptoms
Symptoms of a Baker’s cyst can vary depending on its size and severity:
- Swelling or a lump behind the knee, sometimes extending to the calf
- Knee stiffness and limited range of motion
- Discomfort or pain, especially when bending or extending the knee
- Sensation of fullness or tightness in the back of the knee
- Rarely, the cyst may rupture, causing sudden sharp pain, swelling, and bruising in the calf
- Symptoms may worsen after physical activity or prolonged standing
Causes
Baker’s cysts are often caused by underlying knee joint problems that increase synovial fluid production:
- Osteoarthritis – degeneration of cartilage leading to inflammation and fluid buildup
- Rheumatoid arthritis – autoimmune inflammation of the knee joint
- Meniscus tears – injuries to the cartilage in the knee that allow fluid to escape
- Knee injuries – sprains, ligament tears, or fractures
- Other joint conditions – such as gout or pseudogout causing inflammation
Risk Factors
Several factors increase the likelihood of developing a Baker’s cyst:
- Age above 40, due to increased risk of arthritis
- History of knee injuries or surgery
- Chronic inflammatory joint diseases like rheumatoid arthritis
- Repetitive knee stress from sports or physically demanding jobs
- Obesity, which places additional strain on the knee joint
Complications
While Baker’s cysts are typically benign, complications can occur if the cyst becomes large or ruptures:
- Rupture leading to fluid leakage into the calf, causing swelling and pain
- Compression of nearby nerves or blood vessels, leading to numbness or circulation problems
- Persistent knee stiffness and reduced mobility
- Misdiagnosis of deep vein thrombosis (DVT) due to calf swelling after rupture
- Recurrence, especially if the underlying joint problem is not addressed
Prevention
Preventing Baker’s cysts involves reducing stress and inflammation in the knee:
- Maintain a healthy weight to decrease joint pressure
- Engage in low-impact exercises such as swimming or cycling
- Strengthen the muscles around the knee to support joint stability
- Avoid repetitive high-impact activities that strain the knee
- Manage chronic conditions like arthritis with medications and lifestyle interventions
- Seek early medical attention for knee injuries to prevent fluid accumulation
Treatment Options in Korea
1. Diagnosis
Korean orthopedic specialists use advanced imaging and clinical evaluation to diagnose Baker’s cysts:
- Ultrasound – to visualize the cyst and assess its size and fluid content
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) – to detect associated knee joint problems such as meniscus tears or ligament injuries
- Physical examination – checking for swelling, tenderness, and knee range of motion
- Aspiration (in rare cases) – fluid may be drawn to confirm diagnosis or relieve pressure
2. Non-Surgical Treatments
Most Baker’s cysts are treated conservatively, especially if asymptomatic or small:
- Rest and activity modification – avoiding activities that worsen swelling
- Ice application – to reduce inflammation and discomfort
- Compression wraps or knee braces – to support the joint and reduce fluid accumulation
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) – for pain relief and inflammation control
- Physical therapy – exercises to strengthen surrounding muscles and improve joint flexibility
3. Minimally Invasive and Surgical Options
For persistent, painful, or large cysts, Korean hospitals provide advanced interventions:
- Aspiration with corticosteroid injection – draining fluid and reducing inflammation in the joint
- Arthroscopic surgery – addressing the underlying joint pathology such as meniscus repair or cartilage debridement, which helps prevent cyst recurrence
- Open surgical excision – rarely required, reserved for cases where other treatments fail
4. Rehabilitation and Recovery
After treatment, patients in Korea receive structured rehabilitation programs to restore knee function:
- Gradual range-of-motion exercises
- Strength training for quadriceps and hamstrings
- Balance and proprioception exercises to prevent future injury
- Pain management and monitoring for signs of recurrence
5. Medical Tourism for Baker’s Cyst Treatment in Korea
Korea is recognized for orthopedic excellence and minimally invasive procedures. International patients benefit from:
- State-of-the-art imaging and arthroscopic surgery
- Experienced orthopedic surgeons specializing in knee disorders
- Comprehensive post-treatment rehabilitation programs
- Efficient and coordinated care for both local and global patients