Overview
Atopic Dermatitis (AD), commonly known as eczema, is a chronic inflammatory skin condition characterized by itchy, dry, and inflamed skin. It often begins in childhood but can persist or start in adulthood. In South Korea, the prevalence of AD has increased, especially in urban areas, due to factors such as pollution, climate, and modern lifestyles. Advanced treatments and skin care options are widely available across Korean dermatology clinics and hospitals.
What is Atopic Dermatitis?
Atopic Dermatitis is an allergic skin disorder and part of the “atopic triad”—alongside allergic rhinitis and asthma. It involves a weakened skin barrier and overactive immune response, leading to chronic inflammation. The disease typically follows a relapsing-remitting course, with flare-ups triggered by irritants, allergens, or stress.
Symptoms
- Intense itching (often worse at night)
- Dry, scaly skin
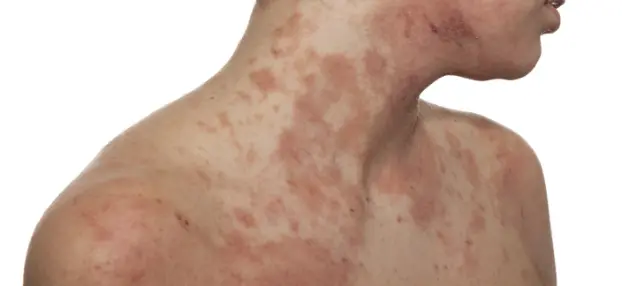
- Red or brownish-gray patches, especially on the hands, feet, ankles, wrists, neck, upper chest, eyelids, and inner elbows/knees
- Thickened, cracked, or oozing skin during flares
- Scratching leads to further skin damage and increases infection risk
Causes
Atopic Dermatitis results from a combination of genetic, immune, and environmental factors:
- Genetics: Mutations in the filaggrin gene weaken the skin barrier
- Immune system dysfunction: Leads to chronic inflammation
- Environmental triggers: Pollutants, allergens, soaps, detergents, and changes in weather
- Microbial imbalance: Overgrowth of bacteria like Staphylococcus aureus on the skin
Risk Factors
- Family history of eczema, asthma, or allergic rhinitis
- Urban living and exposure to air pollution
- Harsh skin care products
- Living in dry or cold climates
- Allergies to foods, dust mites, or pets
Complications
- Skin infections (bacterial, viral, fungal)
- Sleep disturbances due to itching
- Psychological stress, anxiety, or depression
- Allergic rhinitis or asthma (atopic march)
- Permanent skin thickening (lichenification) from chronic scratching
Prevention
- Moisturize regularly to protect the skin barrier
- Avoid known triggers (e.g., soaps, allergens, wool fabrics)
- Maintain a stable indoor environment with humidity control
- Early intervention for symptoms can prevent severe flares
- Use mild, fragrance-free products for skin and laundry
Treatment Options in Korea
South Korea offers world-class dermatology care, combining advanced treatments, personalized skin care regimens, and cosmetic technologies. Atopic Dermatitis is commonly treated in dermatology clinics, hospitals, and even integrated Oriental medicine clinics.
1. Diagnosis
- Based on clinical examination and patient history
- May include:
- Skin patch testing for allergies
- Blood tests for IgE levels
- Skin biopsy in rare or unclear cases
2. Topical Treatments
- Moisturizers (emollients): Essential for restoring skin barrier
- Topical corticosteroids: First-line anti-inflammatory treatment during flares
- Topical calcineurin inhibitors (e.g., Tacrolimus, Pimecrolimus): Non-steroidal options for sensitive areas
- Korean skin barrier creams enriched with ceramides, often prescribed or available OTC
3. Systemic Medications
- For moderate to severe cases:
- Oral antihistamines for itch control
- Oral corticosteroids for short-term flare suppression
- Immunosuppressants (e.g., cyclosporine) under specialist supervision
- Biologics: Dupilumab (Dupixent) is available in Korea and approved for moderate-to-severe AD
4. Phototherapy
- Narrowband UVB (NB-UVB) therapy is widely offered in Korean hospitals
- Reduces inflammation and itch through controlled light exposure
5. Oriental Medicine and Integrative Therapies
- Traditional Korean Medicine clinics may offer:
- Herbal ointments
- Acupuncture
- Moxibustion therapy
- Personalized dietary plans
- These are sometimes combined with Western dermatology in integrated clinics
6. Skin Care and Lifestyle Management
- Customized regimens based on skin type
- Korea has a wide range of eczema-safe cosmetics and cleansers
- Educational programs in hospitals to train patients and parents on flare prevention
7. Pediatric Dermatology
- Specialized care for infants and children available at top-tier hospitals like Seoul National University Hospital, Asan Medical Center, and Severance
- Multidisciplinary teams address diet, skin care, and psychosocial impact