Overview
Astigmatism is a common refractive error that causes blurred or distorted vision due to an irregular curvature of the cornea or lens. Unlike nearsightedness or farsightedness, astigmatism affects vision at all distances. In South Korea, advancements in eye care technologies, including laser correction surgeries and premium lenses, have made treatment options widely accessible and highly effective.
What is Astigmatism?
Astigmatism is a vision condition that occurs when the cornea (the clear front surface of the eye) or the lens inside the eye has an uneven curvature. Instead of having a round shape like a basketball, the surface is shaped more like a football, causing light to focus unevenly on the retina. This leads to blurred or distorted vision at both near and far distances.
Astigmatism often occurs along with other refractive errors like myopia (nearsightedness) or hyperopia (farsightedness).
Symptoms
- Blurred or distorted vision
- Eyestrain or discomfort
- Headaches
- Difficulty seeing at night
- Squinting
- Double vision in severe cases
Causes
- Irregular Corneal Shape: Most common cause, usually present from birth
- Lens Deformity: Less common but can also lead to astigmatism
- Eye Injuries: Trauma that changes the shape of the cornea
- Surgery: Some eye surgeries can result in astigmatism
- Keratoconus: A degenerative condition that leads to severe astigmatism
Risk Factors
- Family history of astigmatism or other refractive errors
- Eye injuries or trauma
- Certain types of eye surgery (e.g., cataract surgery)
- Progressive eye diseases (e.g., keratoconus)
- Excessive eye rubbing
Complications
- Chronic eyestrain and fatigue
- Poor academic or work performance due to visual difficulty
- Risk of amblyopia (lazy eye) in children if left untreated
- Headaches from constant squinting
- Reduced quality of life due to visual distortion
Prevention
Astigmatism cannot be entirely prevented, especially when it is congenital, but some precautions can help reduce progression:
- Regular eye exams for early detection
- Avoid excessive eye rubbing
- Wear protective eyewear to prevent trauma
- Use prescribed corrective lenses as advised
- Monitor children’s vision for early intervention
Treatment Options in Korea
South Korea offers world-class eye care services and is a global hub for ophthalmologic surgeries. Patients have access to cutting-edge diagnostics and treatment options.
1. Diagnosis
- Visual Acuity Test: Measures clarity of vision
- Keratometry: Measures curvature of the cornea
- Corneal Topography: Maps the surface curvature in detail
- Refraction Test: Identifies exact lens prescription
2. Corrective Lenses
- Eyeglasses: Customized prescription lenses to correct light focus
- Contact Lenses: Toric lenses designed specifically for astigmatism
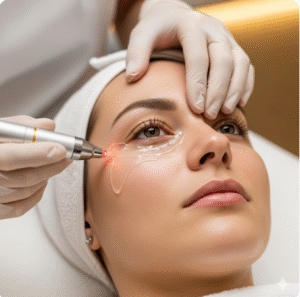
3. Laser Eye Surgery
- LASIK (Laser-Assisted In Situ Keratomileusis): Reshapes the cornea for long-term correction
- LASEK and PRK: Alternatives for patients with thinner corneas
- SMILE (Small Incision Lenticule Extraction): Minimally invasive laser option growing in popularity in Korea
4. Refractive Lens Exchange (RLE)
- Surgical option for older patients or those not eligible for laser correction
- Involves replacing the eye’s natural lens with a customized intraocular lens (IOL)
5. Pediatric Vision Care
- Specialized clinics offer early diagnosis and treatment for children
- Use of corrective glasses or contact lenses to prevent developmental complications