Overview
Arthropathy is a general term used to describe any disease of the joints. It encompasses a wide range of joint disorders, including inflammatory, degenerative, and metabolic conditions. Arthropathy can result in joint pain, stiffness, swelling, and restricted movement. Depending on the underlying cause, it can affect one or multiple joints and vary in severity from mild discomfort to disabling deformity.
What is Arthropathy?
Arthropathy refers to joint disease in general and includes conditions such as osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, gout, psoriatic arthritis, septic arthritis, and neuropathic arthropathy (Charcot joint). Some arthropathies are due to systemic diseases, such as lupus or diabetes, while others are caused by injury, infection, or genetic disorders.
Common types of arthropathy include:
- Degenerative Arthropathy (e.g., Osteoarthritis)
- Inflammatory Arthropathy (e.g., Rheumatoid arthritis, Psoriatic arthritis)
- Crystal-induced Arthropathy (e.g., Gout, Pseudogout)
- Neuropathic Arthropathy (e.g., Charcot joint due to diabetes or nerve damage)
- Infectious Arthropathy (e.g., Septic arthritis)
Symptoms
- Joint pain
- Swelling or fluid buildup
- Morning stiffness or stiffness after inactivity
- Redness or warmth around the affected joint
- Limited joint mobility
- Joint deformity (in advanced or chronic conditions)
Symptoms can be intermittent or persistent and may worsen over time without treatment.
Causes
- Aging and wear-and-tear of cartilage (degenerative)
- Autoimmune diseases (rheumatoid arthritis, lupus)
- Metabolic disorders (gout, pseudogout)
- Nerve damage (as in diabetic neuropathy)
- Infections (bacterial, viral, or fungal arthritis)
- Trauma or repetitive stress injuries
- Genetic factors influencing bone or immune system health
Risk Factors
- Age (risk increases with age)
- Gender (some forms more common in women, e.g., RA)
- Obesity
- Family history of joint disorders
- Previous joint injuries
- Chronic illnesses like diabetes or autoimmune diseases
- Poor immune system function
Complications
- Chronic pain and joint stiffness
- Loss of joint function and mobility
- Joint deformities
- Need for surgical intervention or joint replacement
- Reduced quality of life
- Systemic effects in inflammatory arthropathies (e.g., organ involvement in RA or lupus)
Prevention
- Maintain a healthy weight to reduce joint strain
- Exercise regularly with low-impact activities
- Avoid repetitive joint strain or overuse
- Treat underlying conditions early (e.g., diabetes, infections)
- Use protective gear to avoid injuries
- Manage chronic inflammation through proper diet and medical care
Treatment Options in Korea
South Korea provides comprehensive care for arthropathy through advanced rheumatology, orthopedics, and rehabilitation services. Hospitals offer both conventional and integrated medicine approaches tailored to the type and severity of joint disease.
- Diagnosis
- Blood tests: For autoimmune markers, inflammation levels, and uric acid
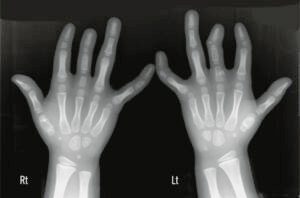
- Imaging: X-rays, MRI, CT scans to detect joint damage or fluid accumulation
- Joint aspiration: Analysis of synovial fluid for infection or crystals
- Nerve studies: In neuropathic arthropathy cases
- Medication
- NSAIDs: For inflammation and pain relief
- Corticosteroids: Oral or intra-articular injections for severe inflammation
- DMARDs: For autoimmune and inflammatory arthropathies (e.g., methotrexate)
- Biologic agents: For patients with resistant autoimmune arthropathies
- Urate-lowering therapy: For gout and pseudogout
- Antibiotics/Antifungals: For infectious arthropathy
- Rehabilitation and Physical Therapy
- Strengthening and flexibility exercises
- Joint protection and assistive devices
- Occupational therapy for daily activity modifications
- Surgery
- Arthroscopic procedures for joint cleaning or repair
- Joint fusion or realignment
- Joint replacement for advanced damage