Overview
Amaurosis Fugax is a temporary loss of vision in one eye caused by a brief interruption of blood flow to the retina. Though the vision returns quickly—typically within minutes—it is a warning sign of serious vascular conditions, such as stroke or arterial blockage. It should never be ignored and always warrants medical evaluation.
What is Amaurosis Fugax?
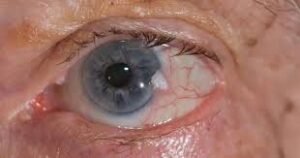
Amaurosis Fugax, meaning “fleeting darkness,” refers to a sudden, transient loss of vision in one eye. Patients often describe it as a curtain descending over their field of vision. The episode usually lasts seconds to a few minutes and resolves on its own. It is most often caused by a small embolus blocking blood flow in the retinal artery.
Symptoms
Symptoms are typically dramatic but brief. They may include:
- Sudden, painless vision loss in one eye
- A gray or black curtain-like shadow moving across the visual field
- Blurred or dimmed vision
- Total or partial blindness
- Spontaneous return of normal vision within minutes
Causes
Amaurosis Fugax is a symptom, not a disease. The most common causes include:
- Emboli from atherosclerotic plaques in the carotid artery
- Clots from the heart (e.g., due to atrial fibrillation or valve disease)
- Inflammatory diseases like giant cell arteritis
- Low blood pressure or poor circulation
- Retinal migraine or optic nerve disorders
Risk Factors
The risk of Amaurosis Fugax increases with:
- Age over 50
- Smoking
- High blood pressure
- High cholesterol
- Diabetes mellitus
- Atrial fibrillation or heart disease
- Family history of stroke or cardiovascular disease
Complications
Although vision usually returns to normal, Amaurosis Fugax is a red flag for more serious issues. Potential complications include:
- Ischemic stroke (often within days or weeks)
- Retinal artery occlusion
- Permanent vision loss (in rare cases)
- Recurrent episodes (if underlying cause isn’t treated)
Prevention
Preventing Amaurosis Fugax means addressing the root vascular risks. Key preventive measures include:
- Blood pressure and cholesterol control
- Smoking cessation
- Diabetes management
- Healthy diet and exercise
- Antiplatelet or anticoagulant medications (if prescribed)
- Regular cardiovascular screenings
Treatment Options in Korea
South Korea is a leader in advanced vascular and neurological care. Patients with Amaurosis Fugax have access to:
- High-resolution imaging (CT angiography, MRI, carotid ultrasound)
- Expert evaluation by neurologists, ophthalmologists, and cardiologists
- Medical therapy with blood thinners (aspirin, clopidogrel, or DOACs)
- Carotid endarterectomy or stenting for arterial blockage
- International patient centers in top hospitals (e.g., Severance, Samsung Medical Center, Asan Medical Center)
- Stroke prevention and lifestyle counseling programs
South Korea’s healthcare system offers modern diagnostics, world-class specialists, and multilingual support, making it an excellent choice for comprehensive management of Amaurosis Fugax.