Overview
Allergic Bronchopulmonary Aspergillosis (ABPA) is a hypersensitivity reaction to a common fungus called Aspergillus fumigatus, which affects the lungs. It mainly occurs in people with asthma or cystic fibrosis. ABPA triggers inflammation in the airways, leading to worsening respiratory symptoms, lung damage, and in some cases, permanent bronchiectasis. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial to avoid long-term complications.
What is Allergic Bronchopulmonary Aspergillosis (ABPA)?
ABPA is a complex allergic condition that arises when the immune system overreacts to the presence of Aspergillus fumigatus, a fungus that thrives in soil, dust, and decaying matter. This reaction causes inflammation, increased mucus production, and airway obstruction. It is not a fungal infection but rather an allergic immune response to the fungus. ABPA mostly affects individuals with preexisting lung conditions, especially asthma and cystic fibrosis.
Symptoms
- Chronic coughing with mucus (may contain brownish plugs)
- Wheezing and shortness of breath
- Chest tightness
- Recurrent asthma attacks
- Low-grade fever
- Fatigue and malaise
- Coughing up blood (in advanced stages)
- Unexplained weight loss
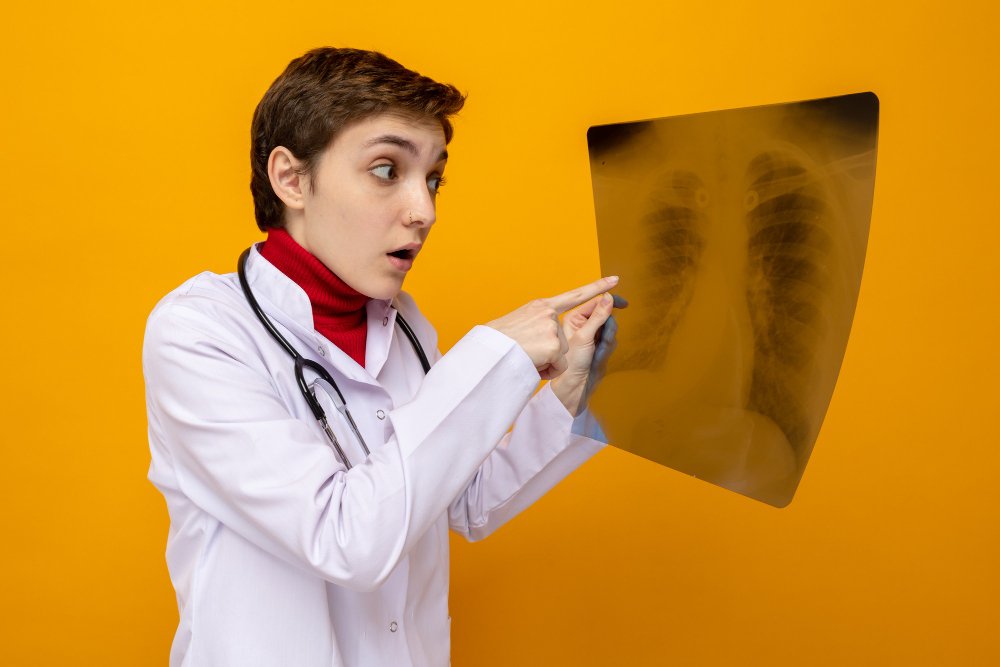
- Repeated pulmonary infiltrates visible on chest X-ray
Causes
ABPA is caused by an exaggerated immune response to inhaled spores of Aspergillus fumigatus. Instead of clearing the spores, the immune system releases inflammatory chemicals, leading to swelling of the airways and damage to lung tissue.
Factors contributing to ABPA include:
- Persistent exposure to moldy environments
- Weakened airway defenses due to asthma or cystic fibrosis
Risk Factors
- Asthma: Moderate to severe asthma increases risk.
- Cystic Fibrosis: A major predisposing condition for ABPA.
- Immunosuppression: People with compromised immunity are more prone to fungal colonization.
- Environmental Exposure: Living or working in damp or moldy environments.
Complications
- Bronchiectasis: Irreversible widening of the airways, leading to chronic infections.
- Lung Scarring: Fibrosis and permanent lung damage from repeated inflammation.
- Respiratory Failure: In untreated severe cases.
- Chronic Fungal Colonization: Risk of chronic aspergillosis or fungal ball (aspergilloma) in damaged lung tissue.
- Decreased Quality of Life: Due to persistent symptoms and reduced lung function.
Prevention
While ABPA cannot be entirely prevented in those predisposed, several measures can reduce risk:
- Control of asthma or cystic fibrosis: Effective management of underlying conditions.
- Avoid moldy environments: Reduce exposure to damp, dusty, or compost-filled areas.
- Air filters: Use of HEPA filters in home or hospital settings.
- Early diagnosis: Regular screening for Aspergillus-specific IgE in high-risk patients.
Treatment Options in Korea
South Korea offers advanced diagnostic and treatment options for ABPA in top-tier respiratory and immunology centers. Management includes:
1. Medication
- Corticosteroids (e.g., Prednisolone): First-line treatment to reduce inflammation.
- Antifungal agents:
- Itraconazole or Voriconazole: Reduce fungal load and help taper steroid use.
- Biologic therapy (for severe/refractory cases):
- Omalizumab (anti-IgE monoclonal antibody)
- Available in specialized allergy/immunology departments
2. Diagnostic Services
- Skin testing and blood tests: To detect Aspergillus-specific IgE and eosinophilia.
- High-resolution CT scan: To evaluate bronchiectasis.
- Offered at major hospitals like:
- Severance Hospital (Yonsei University)
- Seoul National University Hospital
- Asan Medical Center
- Samsung Medical Center
3. Pulmonary Rehabilitation
- Breathing exercises and physiotherapy to clear mucus and improve lung function.
- Available at dedicated rehab units across Korea.
4. Regular Monitoring
- Periodic chest X-rays and pulmonary function tests.
- Regular follow-up with pulmonologists to adjust medication.
5. Patient Education
- Asthma self-management training
- Guidance on mold avoidance and environmental hygiene