Overview
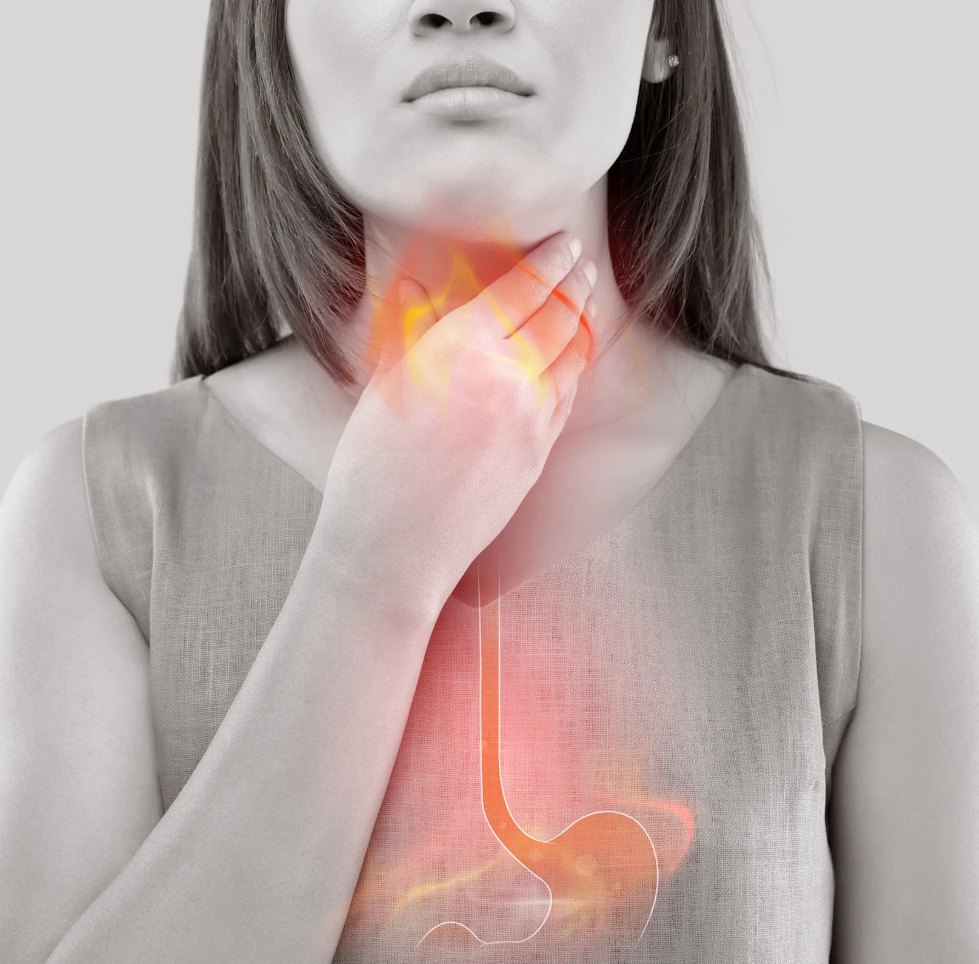
Acid reflux is a common digestive condition that occurs when stomach acid flows backward into the esophagus, the tube that connects the throat to the stomach. This backflow, known as gastroesophageal reflux, can irritate the lining of the esophagus and cause symptoms such as heartburn, chest discomfort, and regurgitation. While occasional acid reflux is normal, frequent episodes may indicate a more serious condition known as GERD (Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease).
What is Acid Reflux?
Acid reflux happens when the lower esophageal sphincter (LES) — a ring of muscle at the end of the esophagus — becomes weak or relaxes inappropriately. This allows stomach acid and partially digested food to move up into the esophagus.
Mild or occasional acid reflux is common, but when symptoms occur two or more times per week or significantly interfere with daily life, it may be diagnosed as GERD.
Symptoms
- Burning sensation in the chest (heartburn), especially after eating or at night
- Sour or bitter taste in the mouth (regurgitation)
- Difficulty swallowing (dysphagia)
- Chest pain or discomfort
- Hoarseness or chronic sore throat
- Coughing or wheezing (especially at night)
- Sensation of a lump in the throat
- Bloating or burping
- Nausea after meals
Causes
Acid reflux is caused by the inappropriate relaxation or weakening of the LES, allowing acid to escape from the stomach into the esophagus. Contributing factors include:
- Overeating or eating large meals
- Lying down soon after eating
- Being overweight or obese
- Smoking
- Pregnancy
- Hiatal hernia
- Certain foods (e.g., spicy, fatty, or acidic foods)
- Drinks like coffee, alcohol, carbonated beverages
- Medications (e.g., NSAIDs, aspirin, calcium channel blockers)
Risk Factors
- Obesity: Increases pressure on the stomach
- Pregnancy: Hormonal changes and pressure on the abdomen
- Smoking: Weakens the LES
- Diet: Frequent consumption of trigger foods
- Sedentary lifestyle
- Family history of GERD
- Frequent use of certain medications
Complications
If acid reflux becomes chronic or severe (as in GERD), it can lead to:
- Esophagitis: Inflammation of the esophagus lining
- Esophageal stricture: Narrowing of the esophagus due to scar tissue
- Barrett’s esophagus: Precancerous changes in esophageal lining
- Esophageal ulcers
- Chronic cough or laryngitis
- Tooth enamel erosion
Prevention
You can reduce the risk of acid reflux through lifestyle and dietary changes:
- Eat smaller, more frequent meals
- Avoid eating 2–3 hours before bedtime
- Elevate the head of your bed
- Maintain a healthy weight
- Avoid trigger foods (e.g., citrus, chocolate, caffeine, spicy foods)
- Quit smoking
- Limit alcohol and carbonated beverages
- Wear loose-fitting clothing around the waist
Treatment Options in korea
1. Lifestyle Modifications:
- Weight loss
- Dietary changes (eliminating trigger foods)
- Avoid lying down after meals
- Elevating the head during sleep
2. Medications:
- Antacids: Neutralize stomach acid (e.g., Tums, Maalox)
- H2 blockers: Reduce acid production (e.g., ranitidine, famotidine)
- Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs): Stronger acid reducers (e.g., omeprazole, esomeprazole)
- Prokinetics: Help strengthen the LES and improve gastric emptying (less commonly used)
3. Surgical Options (for severe cases):
- Fundoplication: The top of the stomach is wrapped around the LES to strengthen it
- LINX device: A magnetic ring placed around the LES to prevent acid reflux