Overview
Japanese Encephalitis Virus (JEV) is a mosquito-borne viral infection that affects the central nervous system, leading to inflammation of the brain (encephalitis). In South Korea, JEV is a public health concern, particularly in rural areas during summer and early autumn when mosquito activity is high. Vaccination programs, mosquito control measures, and advanced hospital care have significantly reduced severe cases.
What is Japanese Encephalitis Virus?
JEV is a flavivirus transmitted primarily by Culex mosquitoes, with pigs and wading birds serving as amplifying hosts. While most infections are asymptomatic or mild, severe cases can cause neurological complications such as seizures, paralysis, and long-term cognitive deficits. JEV is a preventable disease, and South Korea has implemented national vaccination programs for children and travelers to endemic areas.
Symptoms
- Fever and headache
- Nausea and vomiting
- Stiff neck
- Seizures, particularly in children
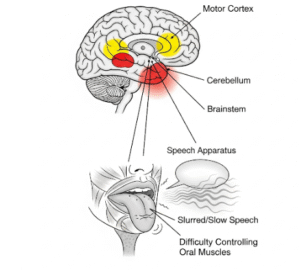
- Muscle weakness or paralysis
- Confusion or altered mental status
- Sensitivity to light (photophobia)
Causes
- Transmission through mosquito bites, primarily Culex species
- Presence of amplifying hosts such as pigs and birds in rural areas
- Seasonal mosquito activity during summer and autumn
- Travel to endemic regions without prior vaccination
Risk Factors
- Children and elderly individuals
- Residents in rural or agricultural areas
- Travelers to endemic regions during peak mosquito season
- Unvaccinated individuals
- Outdoor activities during evening and night when mosquitoes are active
Complications
- Severe neurological damage including seizures, paralysis, or coma
- Long-term cognitive or motor impairments
- Death in severe cases, though rare in Korea due to prompt medical care
- Secondary infections due to hospitalization or weakened immunity
Prevention
- Vaccination: South Korea offers routine JEV immunization for children and at-risk travelers
- Mosquito control: Reducing standing water and using insecticides in endemic areas
- Personal protection: Wearing protective clothing, using insect repellents, and mosquito nets
- Avoiding outdoor activities during peak mosquito activity
Treatment Options in Korea
There is no specific antiviral treatment for JEV, so management focuses on supportive care:
- Diagnosis:
- Blood tests and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) analysis
- PCR testing and serology to detect JEV antibodies
- Neuroimaging (MRI or CT) to assess brain involvement
- Medical Management:
- Supportive care in hospitals for severe cases
- Management of fever, seizures, and neurological symptoms
- Intravenous fluids and respiratory support if needed
- Intensive care for critically ill patients
- Vaccination Programs:
- Routine childhood vaccination through national immunization schedules
- Travel vaccination for at-risk individuals
- Follow-up for immunity monitoring in high-risk populations
- Specialized Care in Korean Hospitals:
- Seoul National University Hospital, Asan Medical Center, and Samsung Medical Center provide advanced supportive care and neurological monitoring
- Pediatric and adult neurology teams manage complications and rehabilitation
- Follow-Up Care:
- Monitoring for neurological sequelae
- Physical and occupational therapy for patients with motor or cognitive impairments
- Education on mosquito avoidance and future vaccination