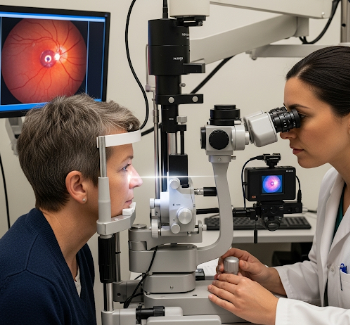
What is Diabetic Eye Screening?
Diabetic eye screening is a specialized examination that detects eye problems caused by diabetes, particularly diabetic retinopathy—a condition where high blood sugar damages the blood vessels of the retina. It is one of the most important preventive health checks for people living with diabetes.
Diabetic retinopathy is the leading cause of vision loss among working-age adults worldwide, but it can be prevented or delayed if diagnosed early. A diabetic eye screening involves detailed imaging of the retina, vision tests, and eye health evaluation, often using advanced technologies like digital fundus photography, optical coherence tomography (OCT), and fluorescein angiography.
In Korea, diabetic eye screening is widely practiced in hospitals, specialized eye clinics, and health centers. The country is recognized for its state-of-the-art ophthalmology departments, where digital imaging and artificial intelligence (AI)-assisted diagnostics help detect eye damage at the earliest stage.
✔️ Identifies diabetic retinopathy before symptoms appear
🔹 Detects related conditions like glaucoma and cataracts
🔸 Protects patients from preventable blindness
Why It’s Done
The primary goal of diabetic eye screening is early detection and prevention of vision loss. Diabetes damages tiny blood vessels in the eye, leading to:
➡️ Diabetic Retinopathy – swelling, leakage, or abnormal blood vessel growth in the retina
➡️ Diabetic Macular Edema (DME) – swelling in the central part of the retina (macula), affecting sharp vision
➡️ Glaucoma – increased eye pressure leading to optic nerve damage
➡️ Cataracts – clouding of the lens, more common in diabetic patients
Reasons why screening is essential:
✔️ Early diagnosis → Treatment is most effective in early stages
✔️ Silent progression → Diabetic retinopathy often has no symptoms until it’s advanced
✔️ Prevents blindness → Timely treatment reduces risk of severe vision loss by up to 95%
✔️ Improves quality of life → Preserves independence and daily activities
In Korea, diabetic patients are strongly encouraged to undergo annual eye screenings, with many health insurance plans covering the test.
Alternatives
While diabetic eye screening is the gold standard, alternative approaches may include:
⭐ Basic Vision Tests – Eye chart exams can reveal reduced vision but may miss early retinal damage
⭐ Self-Monitoring at Home – Patients can monitor changes in vision, but early disease often has no symptoms
⭐ General Eye Exams by Optometrists – Useful, but not as detailed as a specialist diabetic eye screening
⭐ AI-based Home Retinal Imaging Devices – Emerging technology, but still less accurate than clinical tests
👉 These alternatives may help but are not a substitute for a comprehensive diabetic eye screening conducted by an ophthalmologist.
Preparation
Patients undergoing diabetic eye screening in Korea usually follow these steps:
🔹 Medical History Review – Details of diabetes duration, blood sugar control, and previous eye issues are recorded
🔹 Medication Adjustment – No major changes are required, but patients should inform doctors about blood pressure or insulin medications
🔹 Fasting Not Required – Screening is non-invasive, so patients can eat and take medicines normally
🔹 Arrange Transportation – Eye drops used for dilation may blur vision for several hours, so driving is not recommended afterward
⭐ Patients are advised to bring sunglasses, as dilated pupils cause light sensitivity
⭐ Blood sugar and blood pressure control before the test improves accuracy and safety
How It’s Done
The process of diabetic eye screening in Korea is typically smooth, efficient, and technology-driven.
- Pupil Dilation
✔️ Eye drops are given to widen pupils
✔️ Allows doctors to examine the retina thoroughly - Digital Retinal Photography
🔹 High-resolution cameras capture detailed images of the retina
🔹 Korean hospitals often use AI-assisted imaging for precise diagnosis - Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT)
➡️ A non-invasive scan that shows cross-sections of the retina
➡️ Detects swelling or fluid accumulation - Fluorescein Angiography (if needed)
🔸 A dye is injected into the arm, and special cameras track blood flow in retinal vessels
🔸 Helps identify leakage or abnormal vessel growth - Visual Acuity & Eye Pressure Tests
✔️ Standard vision chart test
✔️ Tonometry used to measure intraocular pressure (important for glaucoma detection) - Consultation & Results
➡️ Doctor explains findings, shows retinal images, and recommends next steps
➡️ If abnormalities are detected, treatment options (laser therapy, injections, or surgery) are discussed
Recovery
Since diabetic eye screening is non-invasive, recovery is quick.
✔️ Temporary Blurred Vision – Due to pupil dilation, may last 4–6 hours
✔️ Light Sensitivity – Sunglasses recommended after leaving the clinic
✔️ Resume Normal Activities – Patients can eat, drink, and return to daily routines
✔️ Driving Restrictions – Avoid driving until vision clears completely
⭐ No downtime is required—patients can typically return to work or normal activities the same day.
Complications
Diabetic eye screening is safe, but rare side effects may include:
⚠️ Mild Stinging – From dilating eye drops
⚠️ Temporary Blurred Vision & Sensitivity – Common but short-lived
⚠️ Allergic Reaction – Very rare, to eye drops or fluorescein dye
⚠️ False Negatives – If pupils are not dilated properly or images are unclear
➡️ In Korea, these risks are minimized with modern non-invasive imaging techniques and skilled ophthalmologists.
Treatment Options in Korea
If diabetic eye screening reveals abnormalities, Korea offers advanced treatment options:
🏥 Laser Photocoagulation – Seals leaking vessels, preventing further damage
🏥 Intravitreal Injections (Anti-VEGF Therapy) – Drugs injected directly into the eye to reduce swelling and abnormal blood vessel growth
🏥 Vitrectomy Surgery – Removes scar tissue and blood from the eye in advanced cases
🏥 Cataract Surgery – Modern phacoemulsification with premium lenses for diabetic cataracts
🏥 Glaucoma Management – Eye drops, laser therapy, or surgery as needed
Why Korea is a Top Destination:
✔️ Cutting-edge technology – OCT, AI-based imaging, robotic-assisted surgeries
✔️ Experienced ophthalmologists – Many trained internationally
✔️ Affordable costs – Screenings and treatments are significantly cheaper than in the US or Europe
✔️ Medical tourism support – Translation services, travel assistance, and bundled health check-up packages
Estimated Costs in Korea:
🔹 Diabetic Eye Screening (Basic) → $40 – $80
🔹 Comprehensive Screening with OCT & Angiography → $150 – $300
🔹 Laser Treatment for Retinopathy → $600 – $1,200 per session
🔹 Intravitreal Injections → $800 – $1,500 per injection
🔹 Vitrectomy Surgery → $4,000 – $6,500
Conclusion
Diabetic eye screening is a life-saving preventive measure for individuals with diabetes. Since diabetic retinopathy and related conditions often progress silently, annual screening is essential for protecting vision.
In Korea, patients benefit from:
✔️ State-of-the-art retinal imaging technology
✔️ Highly skilled ophthalmologists with global expertise
✔️ Affordable screening and treatment options
✔️ Comprehensive medical tourism support for international patients
👉 By choosing diabetic eye screening in Korea, patients can ensure early detection, timely treatment, and long-term preservation of vision.
Remember: Diabetes management is incomplete without regular eye screening. Protecting your vision today ensures a healthier, more independent future.