What is an Electrocardiogram (ECG)?
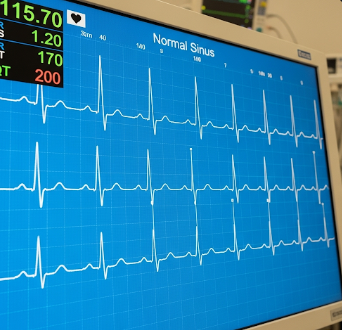
An electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) is a non-invasive test that measures the electrical activity of the heart. It provides crucial information about the heart’s rhythm, rate, and conduction pathways, helping detect abnormalities such as arrhythmias, ischemia, or previous heart attacks.
There are different types of ECGs:
✔️ Resting ECG – Standard test performed while the patient is at rest
🔹 Exercise (Stress) ECG – Monitors heart activity during physical exertion
🔸 Holter Monitoring – Continuous recording for 24–48 hours to detect intermittent arrhythmias
🔹 Event Monitors – Activated by patients when symptoms occur
🔸 Wireless or Wearable ECG Devices – Remote monitoring for long-term evaluation
In Korea, ECGs are widely available in hospitals, cardiology clinics, and health screening centers. The country is recognized for advanced digital ECG machines, AI-assisted interpretation, and highly skilled cardiologists, providing accurate and timely diagnosis.
➡️ Detects heart rhythm disturbances
➡️ Identifies ischemic changes or previous heart attacks
➡️ Monitors effectiveness of cardiac medications
Why It’s Done
ECGs are performed to assess heart health, diagnose conditions, and guide treatment.
✔️ Detect arrhythmias – Atrial fibrillation, tachycardia, bradycardia, and conduction blocks
✔️ Diagnose ischemic heart disease – Signs of reduced blood flow or heart attack
✔️ Monitor ongoing heart conditions – Heart failure, post-surgery, or pacemaker function
✔️ Screen for congenital or structural abnormalities – Especially in high-risk individuals
✔️ Evaluate symptoms – Chest pain, palpitations, dizziness, or syncope
Medical Benefits:
➡️ Early detection of cardiac disease → Improves prognosis and treatment outcomes
➡️ Non-invasive and quick → Minimal risk and immediate results
➡️ Guides interventions → Medication adjustments, procedures, or lifestyle changes
In Korea, ECG is commonly included in annual health check-ups and cardiac risk assessments for people with hypertension, diabetes, high cholesterol, or a family history of heart disease.
Alternatives
While ECG is effective for evaluating electrical activity, other tests provide additional or complementary information:
⭐ Echocardiography – Visualizes heart structure, valves, and function
⭐ Stress Echocardiogram – Assesses heart function under exercise
⭐ Cardiac MRI – Detailed imaging of cardiac tissue and structure
⭐ Holter or Event Monitoring – For intermittent or elusive arrhythmias
⭐ CT Coronary Angiography – Evaluates coronary artery blockages
👉 ECG remains the first-line, cost-effective, and non-invasive test for heart rhythm and conduction evaluation.
Preparation
Preparation for an ECG is simple and mostly involves:
🔹 Avoid applying lotions or oils on the chest – Electrodes require good skin contact
🔹 Wear comfortable, loose clothing – Easy access to the chest area
🔹 Avoid caffeine or vigorous exercise – Especially for stress ECGs
🔹 Inform the technician of medications – Some drugs can affect heart rhythm
⭐ No fasting is required for resting ECG
⭐ Stress ECG may require special footwear and light clothing for exercise
How It’s Done
The procedure is quick, painless, and involves several key steps:
- Electrode Placement
✔️ Small adhesive electrodes placed on the chest, arms, and legs
✔️ Ensure good skin contact for accurate signal detection - Recording Electrical Activity
🔹 Resting ECG – Patient lies quietly while the machine records heart signals for 5–10 minutes
🔹 Stress ECG – Patient walks on a treadmill or pedals a stationary bike while heart activity is monitored
🔹 Holter/Event Monitoring – Portable devices record heart rhythm continuously for 24–48 hours or longer - Analysis & Reporting
➡️ Cardiologist evaluates rhythm, rate, conduction, and signs of ischemia
➡️ AI-assisted interpretation may provide preliminary analysis
Highlights:
✔️ Quick and non-invasive
✔️ Immediate or short-term results
✔️ Safe for repeated use
Recovery
Recovery from an ECG is immediate, as it is non-invasive:
✔️ Resume normal activities immediately
✔️ Minor skin irritation – Rarely at electrode sites
✔️ Stress ECG – Light rest may be recommended after exertion
⭐ Holter/Event monitoring requires careful handling but poses no recovery issues
⭐ Patients may continue medications unless instructed otherwise
Complications
ECG is generally safe with minimal risk:
⚠️ Skin irritation – From adhesive electrodes
⚠️ Mild discomfort during stress ECG – Fatigue or shortness of breath may occur
⚠️ Rare arrhythmia induction – During stress testing, monitored closely
⚠️ Electrode displacement – Can cause inaccurate readings
➡️ In Korea, trained technicians and modern ECG machines minimize these risks.
Treatment Options in Korea
If ECG shows abnormalities, Korea offers comprehensive cardiac treatment:
🏥 Medical Therapy – Antiarrhythmics, anticoagulants, beta-blockers, or ACE inhibitors
🏥 Interventional Cardiology – Angioplasty, stent placement, or pacemaker implantation
🏥 Cardiac Surgery – For structural heart disease or complex arrhythmias
🏥 Lifestyle Modification Programs – Diet, exercise, stress management
🏥 Regular Monitoring – Follow-up ECGs, Holter monitoring, and echocardiograms
Why Korea is a Preferred Destination:
✔️ Advanced diagnostic technology – Digital ECG, AI interpretation, and integrated cardiac care
✔️ Expert cardiologists and electrophysiologists – Internationally trained
✔️ Affordable costs – Lower than Western countries with high-quality care
✔️ Medical tourism support – Translation services, travel assistance, and coordinated care packages
Approximate Costs in Korea:
🔹 Resting ECG → $30 – $60
🔹 Stress ECG → $80 – $150
🔹 Holter Monitoring (24–48 hours) → $100 – $250
🔹 Event Monitor / Wearable ECG → $150 – $400
Conclusion
An Electrocardiogram (ECG) is an essential diagnostic tool for evaluating heart rhythm, rate, and electrical activity. It helps:
✔️ Detect arrhythmias early
✔️ Identify signs of ischemia or heart attack
✔️ Guide treatment decisions for medications, procedures, or lifestyle interventions
✔️ Monitor ongoing cardiac health
In Korea, patients benefit from:
✔️ State-of-the-art ECG machines and digital diagnostics
✔️ Highly skilled cardiologists and electrophysiologists
✔️ Affordable and accessible cardiac testing
✔️ Comprehensive follow-up and care programs
👉 ECGs are a safe, non-invasive, and invaluable tool for maintaining heart health, enabling timely interventions and improving long-term outcomes.
Key Message: Electrocardiography provides crucial insight into cardiac health, guiding both preventive and therapeutic care.