What is an Endoscopy?
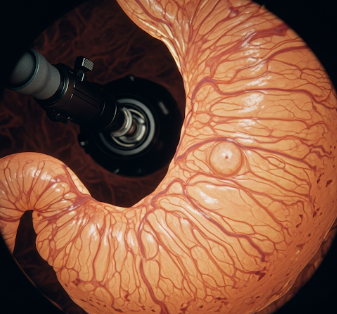
An endoscopy is a medical procedure that allows doctors to view the inside of the digestive tract or other hollow organs using a flexible tube called an endoscope, which has a camera and light at its tip.
💡 Types of Endoscopy include:
✔️ Upper gastrointestinal (GI) endoscopy / Gastroscopy – Examines the esophagus, stomach, and duodenum
✔️ Colonoscopy – Examines the colon and rectum
✔️ Sigmoidoscopy – Examines the lower part of the colon
✔️ Bronchoscopy – Examines the airways and lungs
✔️ Capsule endoscopy – Swallowed camera capsule captures images of the small intestine
Purpose:
➡️ Detect abnormalities – Ulcers, inflammation, tumors, polyps, or bleeding
➡️ Assist in diagnosis – Provides tissue samples (biopsy) for lab analysis
➡️ Guide treatment – Polyp removal, stent placement, or foreign body extraction
In Korea, endoscopy is widely available in hospitals, specialized gastroenterology clinics, and advanced diagnostic centers, with access to high-definition imaging, sedation options, and therapeutic endoscopy.
Why It’s Done
Endoscopy is performed to diagnose, monitor, and sometimes treat gastrointestinal or airway conditions.
✔️ Diagnose digestive disorders – Gastritis, ulcers, GERD, Barrett’s esophagus
✔️ Detect cancer early – Stomach, colon, esophageal, or pancreatic cancer
✔️ Investigate unexplained symptoms – Abdominal pain, bleeding, chronic cough, or swallowing difficulties
✔️ Therapeutic interventions – Polyp removal, dilation of strictures, stent placement
✔️ Monitor chronic conditions – Inflammatory bowel disease, Barrett’s esophagus, or ulcers
Benefits:
➡️ Minimally invasive – Avoids large incisions
➡️ Accurate diagnosis – Direct visualization and biopsy capability
➡️ Therapeutic potential – Immediate treatment during examination
➡️ Early detection of malignancy – Significantly improves prognosis
In Korea, endoscopy is a standard part of health screening, particularly for gastric cancer due to its high prevalence in East Asia.
Alternatives
Alternative diagnostic tools may be considered when endoscopy is unavailable or not suitable:
⭐ Imaging studies – CT scan, MRI, or ultrasound
⭐ Barium swallow / Barium enema – X-ray studies for the esophagus, stomach, or colon
⭐ Capsule endoscopy – Non-invasive imaging for small intestine when conventional endoscopy is difficult
⭐ Non-invasive breath or stool tests – For H. pylori infection or gastrointestinal bleeding
👉 Key Point: While alternatives provide valuable information, endoscopy remains the gold standard for diagnosis and therapeutic interventions in GI and airway disorders.
Preparation
Preparation depends on the type of endoscopy:
🔹 Upper GI endoscopy (gastroscopy)
- Avoid food and drink for 6–8 hours before the procedure
- Arrange for transportation if sedation is used
🔹 Colonoscopy
- Clear liquid diet 1–2 days before the procedure
- Bowel cleansing with prescribed laxatives
- Avoid certain medications – Blood thinners, iron supplements
🔹 Bronchoscopy
- Avoid eating or drinking for several hours
- Inform doctor of respiratory or heart conditions
⭐ Discuss medications and allergies
⭐ Arrange post-procedure care if sedation or anesthesia is administered
How It’s Done
Endoscopy is performed by trained gastroenterologists, pulmonologists, or specialized surgeons:
- Sedation / Anesthesia
✔️ Local anesthetic spray or mild sedation for comfort
✔️ In some cases, general anesthesia may be used - Insertion of Endoscope
🔹 Upper GI – Through mouth to stomach and duodenum
🔹 Colonoscopy – Through the rectum to colon
🔹 Bronchoscopy – Through nose or mouth to the airways - Visualization and Intervention
➡️ Camera transmits real-time images to a monitor
➡️ Biopsies or tissue removal may be performed
➡️ Therapeutic procedures like polyp removal, dilation, or stent placement
Highlights:
✔️ Minimally invasive and highly accurate
✔️ Diagnostic and therapeutic capabilities combined
✔️ Procedure duration – Usually 15–60 minutes depending on type
Recovery
Recovery depends on sedation and procedure type:
✔️ Sedation wear-off – Usually a few hours; patient should rest
✔️ Mild throat or abdominal discomfort – Common after upper GI endoscopy or colonoscopy
✔️ Resume normal diet – As advised by the doctor
✔️ Monitor for complications – Bleeding, pain, fever
⭐ Follow-up – Results of biopsies or polyp removal may take several days
⭐ Return to work or daily activities – Usually next day for routine procedures
Complications
Endoscopy is generally safe, but risks include:
⚠️ Bleeding – Especially after biopsy or polyp removal
⚠️ Perforation – Rare but serious, may require surgery
⚠️ Infection – Rare, precautions are taken with sterilized equipment
⚠️ Sedation-related complications – Respiratory depression or allergic reactions
➡️ In Korea, highly trained specialists, advanced equipment, and strict infection control minimize risks.
Treatment Options in Korea
Korean hospitals offer comprehensive endoscopic services:
🏥 Diagnostic Endoscopy – Gastroscopy, colonoscopy, bronchoscopy, capsule endoscopy
🏥 Therapeutic Endoscopy – Polyp removal, hemostasis, stent placement, dilation of strictures
🏥 Advanced Imaging Endoscopy – Narrow-band imaging, chromoendoscopy, endoscopic ultrasound
🏥 Screening Programs – Gastric and colon cancer screening widely available
🏥 Home Care & Follow-up – Post-procedure care, monitoring, and dietary guidance
Why Korea is a Preferred Destination:
✔️ State-of-the-art endoscopic equipment – High-definition imaging, advanced therapeutic tools
✔️ Expert gastroenterologists and pulmonologists – Extensive experience in diagnosis and treatment
✔️ Early detection programs – Gastric and colon cancer screening for at-risk populations
✔️ Affordable care – Lower costs compared to Western countries with comparable quality
✔️ Medical tourism support – Translation, travel coordination, and hospital assistance
Approximate Costs in Korea:
🔹 Upper GI Endoscopy → $100 – $200
🔹 Colonoscopy → $150 – $300
🔹 Capsule Endoscopy → $400 – $600
🔹 Therapeutic Endoscopy → $200 – $500
🔹 Hospital consultation and sedation → $50 – $100
Conclusion
Endoscopy is a crucial procedure for diagnosing, monitoring, and treating gastrointestinal and airway disorders.
It helps:
✔️ Detect abnormalities like ulcers, polyps, or tumors early
✔️ Provide immediate treatment through minimally invasive techniques
✔️ Guide ongoing medical care for chronic GI or respiratory conditions
✔️ Improve patient outcomes through early detection and intervention
In Korea, patients benefit from:
✔️ Advanced endoscopic technology and imaging systems
✔️ Highly skilled specialists
✔️ Integrated diagnostic and therapeutic services
✔️ Affordable, accessible, and safe care
👉 Key Message: Endoscopy in Korea provides accurate diagnosis, effective treatment, and early detection of serious conditions, making it a vital tool for digestive and respiratory health.