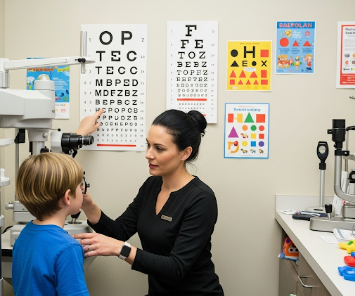
What is Eye Testing for Children?
Eye tests for children are specialized examinations designed to assess vision, eye health, and visual development in infants, toddlers, and school-aged children. Early detection of vision problems is crucial because unaddressed eye issues can affect learning, coordination, and overall development.
💡 Common Pediatric Eye Tests Include:
✔️ Visual acuity test – Measures clarity of vision
✔️ Refraction test – Determines the need for glasses
✔️ Strabismus check – Detects misalignment of eyes
✔️ Amblyopia screening – “Lazy eye” evaluation
✔️ Eye health exam – Checks the retina, optic nerve, and eye structures
✔️ Color vision test – Detects color blindness
✔️ Ocular motility test – Assesses eye movement and coordination
In Korea, pediatric eye care is integrated into hospitals, specialized eye clinics, and school health programs, using advanced diagnostic tools and child-friendly approaches.
Why It’s Done
Early eye testing is essential to identify and correct vision problems before they impact learning and development.
✔️ Detect refractive errors – Myopia, hyperopia, astigmatism
✔️ Identify strabismus or amblyopia – Prevent long-term vision impairment
✔️ Monitor eye development – Ensure normal ocular growth and function
✔️ Prevent complications – Early intervention reduces risk of permanent visual impairment
✔️ Support academic performance – Clear vision is essential for reading, writing, and classroom activities
Clinical Benefits:
➡️ Early detection → Corrective measures such as glasses or patching for lazy eye
➡️ Prevent vision loss → Timely intervention in eye diseases
➡️ Support healthy development → Proper visual function contributes to motor and cognitive development
➡️ Peace of mind for parents → Regular checkups ensure child eye health
In Korea, regular pediatric eye screenings are recommended at ages 6 months, 1 year, 3 years, and school entry, with additional checks if problems are detected.
Alternatives
When standard eye testing is difficult, especially in infants or uncooperative children, alternatives include:
⭐ Autorefractors – Automated devices measuring refractive errors quickly
⭐ Photoscreening – Uses cameras to detect eye alignment and refractive errors in very young children
⭐ Cover-uncover test – Detects strabismus without high-tech equipment
⭐ Home vision screening tools – Simple charts or apps for preliminary assessment
👉 Key Point: While alternatives are helpful for preliminary screening, comprehensive eye exams by pediatric ophthalmologists remain the gold standard.
Preparation
Preparation depends on the child’s age and the type of eye test:
🔹 Parents should provide medical history – Previous eye problems, family history of vision issues, and developmental milestones
🔹 Bring any previous eye prescription or glasses – Helps comparison and tracking
🔹 Explain the procedure in a child-friendly manner – Reduces anxiety and improves cooperation
🔹 Avoid eye drops unless prescribed – Some tests may require dilating drops administered at the clinic
⭐ Comfort items – Favorite toy or pacifier can help infants and toddlers remain calm
⭐ Timing – Schedule the appointment when the child is alert and not tired
How It’s Done
Pediatric eye tests are performed using age-appropriate, non-invasive techniques:
- Visual Acuity Test
✔️ Children identify letters, symbols, or pictures on a chart
✔️ For infants, fixation and tracking responses are observed - Refraction Test
🔹 Measures light focusing on the retina to determine the need for glasses
🔹 May involve autorefractors or retinoscopy - Eye Alignment & Movement Tests
➡️ Cover-uncover and Hirschberg tests – Detect strabismus
➡️ Ocular motility tests – Assess coordinated eye movement - Slit Lamp & Fundus Examination
✔️ Examines cornea, lens, retina, and optic nerve
✔️ Detects structural abnormalities, infections, or congenital issues - Color Vision and Depth Perception
✔️ Ishihara plates or child-friendly color games
✔️ Evaluates ability to distinguish colors and judge depth
Highlights:
✔️ Non-invasive and safe
✔️ Tailored to age and developmental stage
✔️ Allows early diagnosis of common pediatric eye conditions
Recovery / Follow-up
Eye tests are generally safe and non-invasive, with no significant recovery time.
✔️ Dilation effects – Some tests require eye drops that may cause blurred vision for a few hours
✔️ Follow-up appointments – Recommended if glasses, patching, or treatments are needed
✔️ Routine monitoring – Children with risk factors may require annual or semi-annual checks
⭐ Parental guidance – Encouraged to monitor visual behavior at home, ensure adherence to treatments, and attend follow-up visits
Complications / Risks
Pediatric eye tests are generally safe, but minor risks include:
⚠️ Temporary discomfort – Eye drops for dilation may sting briefly
⚠️ Light sensitivity – Eyes may be sensitive after dilation
⚠️ Anxiety or fear – Some children may resist unfamiliar equipment or procedures
⚠️ Misinterpretation – Very young children may provide inaccurate responses, requiring repeat testing
➡️ In Korea, trained pediatric ophthalmologists and child-friendly clinics minimize stress and improve test accuracy.
Treatment Options in Korea
Korea offers comprehensive pediatric eye care, including diagnosis, treatment, and ongoing monitoring:
🏥 Specialized Pediatric Ophthalmology Clinics – Focused on child-friendly care and advanced diagnostics
🏥 Hospital Eye Departments – Equipped with autorefractors, fundus cameras, and slit lamps for pediatric patients
🏥 Vision Correction Treatments – Prescription glasses, contact lenses, and refractive surgery for adolescents
🏥 Therapies for Amblyopia and Strabismus – Eye patching, vision therapy, and surgical correction
🏥 School Screening Programs – Nationwide initiatives to detect vision problems early
Why Korea is a Preferred Destination:
✔️ Advanced diagnostic technology – High-resolution imaging and automated screening
✔️ Experienced pediatric ophthalmologists – Extensive training in child eye care
✔️ Comprehensive treatment options – From glasses to corrective surgery and therapy
✔️ Child-friendly clinics – Reduces anxiety and improves cooperation
✔️ Follow-up and monitoring – Ensures long-term eye health and development
Approximate Costs in Korea:
🔹 Routine Pediatric Eye Exam → $50 – $100
🔹 Refraction / Glasses Prescription → $30 – $70
🔹 Amblyopia Therapy / Eye Patching → $50 – $150
🔹 Strabismus Surgery → $1,500 – $5,000 depending on complexity
🔹 Advanced imaging or specialized testing → $100 – $300
Conclusion
Pediatric eye tests are essential for early detection, treatment, and prevention of vision problems.
They help children:
✔️ Develop normal visual function
✔️ Avoid learning difficulties caused by uncorrected vision problems
✔️ Prevent permanent eye conditions like amblyopia or strabismus
✔️ Receive timely intervention for chronic or congenital eye disorders
In Korea, children benefit from:
✔️ State-of-the-art diagnostic equipment
✔️ Specialized pediatric ophthalmologists
✔️ Comprehensive treatment and follow-up services
✔️ Child-friendly, safe, and effective care
👉 Key Message: Eye tests for children in Korea ensure healthy vision, early intervention, and overall well-being, supporting a lifetime of visual health and development.