What is First Aid?
First aid refers to the immediate care provided to a person who is injured or suddenly becomes ill, before professional medical treatment is available. Its main goal is to preserve life, prevent conditions from worsening, and promote recovery.
💡 Key Components of First Aid Include:
✔️ CPR (Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation) – Restores circulation and breathing in cardiac arrest
✔️ Wound Care – Cleaning, dressing, and controlling bleeding
✔️ Burn Management – Cooling, dressing, and preventing infection
✔️ Fracture and Sprain Management – Immobilization and support
✔️ Choking Relief – Heimlich maneuver or back blows for airway obstruction
✔️ Poisoning Response – Identification and initial interventions
Key Principle: First aid does not replace professional medical care but bridges the time until emergency services or healthcare professionals arrive.
In Korea, first aid is widely promoted in schools, workplaces, hospitals, and public spaces, with government-supported programs and trained volunteers.
Why It’s Done / Importance
First aid is critical to reduce morbidity and mortality in emergencies.
✔️ Preserve life – Immediate intervention can prevent death in cardiac arrest, choking, or severe bleeding
✔️ Prevent complications – Proper wound care and immobilization prevent infection or permanent injury
✔️ Reduce recovery time – Early intervention supports faster healing and rehabilitation
✔️ Enhance public safety awareness – Training empowers communities to respond effectively
✔️ Support emergency services – Immediate aid stabilizes patients for hospital treatment
Clinical and Social Benefits:
➡️ Timely intervention → Can mean the difference between life and death
➡️ Minimizes disability → Proper immobilization and wound management reduce long-term harm
➡️ Community preparedness → More people trained in first aid leads to safer environments
➡️ Peace of mind → Families and workplaces feel safer knowing first aid is available
In Korea, first aid training is integrated into school curriculums, workplace safety programs, and national campaigns, ensuring widespread knowledge and preparedness.
Alternatives / Emergency Measures
When immediate first aid is not possible, alternative emergency measures include:
⭐ Calling emergency services (119 in Korea) – Professional medical response
⭐ Using automated external defibrillators (AEDs) – Publicly accessible for cardiac emergencies
⭐ Safety measures and preventive actions – Fire alarms, workplace safety protocols, or protective equipment
⭐ Telemedicine guidance – Remote instructions from medical professionals
👉 Key Point: While first aid is often the first response, emergency services and professional care are essential for definitive treatment.
Preparation
Preparation for effective first aid includes knowledge, equipment, and readiness:
🔹 Training and certification – CPR, basic life support (BLS), wound care, and emergency response courses
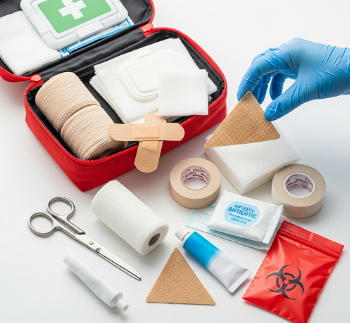
🔹 First aid kits – Stocked with bandages, antiseptics, gloves, scissors, adhesive tape, burn gel, and splints
🔹 AED awareness – Knowledge of locations and operation of automated defibrillators
🔹 Emergency plan – Clear procedures for schools, homes, workplaces, and public spaces
⭐ Regular drills and refresher courses – Maintain skill levels and confidence
⭐ Personal protective equipment (PPE) – Gloves, masks, and eye protection for safety during care
How It’s Done
First aid procedures vary depending on the emergency. Basic principles include assessing the situation, providing immediate care, and seeking professional help.
- Assessment and Safety
✔️ Ensure scene safety – Protect yourself and the patient
✔️ Assess responsiveness, airway, breathing, and circulation (ABC) - Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR)
🔹 For unresponsive patients without breathing
🔹 Chest compressions and rescue breaths (or hands-only CPR for adults)
🔹 Use AED if available - Bleeding Control
➡️ Apply direct pressure to wounds
➡️ Use sterile dressings or bandages
➡️ Elevate limb if possible to reduce bleeding - Burn Management
✔️ Cool burn under running water for 10–20 minutes
✔️ Cover with sterile, non-adhesive dressing
✔️ Avoid ice or creams unless instructed - Fracture or Sprain Management
🔹 Immobilize using splints or slings
🔹 Avoid unnecessary movement
🔹 Apply ice to reduce swelling - Choking Relief
➡️ Back blows and abdominal thrusts (Heimlich maneuver)
➡️ Encourage coughing if partially obstructed - Poisoning or Exposure
✔️ Identify substance if possible
✔️ Contact Poison Control Center
✔️ Avoid inducing vomiting unless instructed
Highlights:
✔️ First aid is immediate, simple, and lifesaving
✔️ Actions should always prioritize safety for both caregiver and patient
✔️ Training enhances confidence and effectiveness
Recovery / Follow-up
After first aid is administered, proper follow-up ensures stability, healing, and prevention of complications:
✔️ Medical evaluation – Hospital or clinic visit for wounds, burns, fractures, or internal injuries
✔️ Monitoring for complications – Infection, bleeding, swelling, or delayed reactions
✔️ Rehabilitation – Physiotherapy for musculoskeletal injuries
✔️ Emotional support – Trauma counseling or stress management after emergencies
✔️ Documentation – Record interventions, time of care, and emergency response for medical teams
⭐ Effective first aid reduces recovery time and improves outcomes significantly.
Complications / Risks
While first aid is generally safe, improper techniques can have consequences:
⚠️ Infection risk – Without gloves or clean dressings
⚠️ Incorrect CPR or choking relief – May cause rib fractures or worsen obstruction
⚠️ Delayed professional care – Failure to seek medical help may worsen injury
⚠️ Allergic reactions – From antiseptics, medications, or environmental exposure
⚠️ Psychological impact – Trauma or anxiety after emergencies
➡️ In Korea, first aid certification programs emphasize safety, correct technique, and emergency escalation to minimize risks.
Treatment / First Aid Services in Korea
Korea offers extensive first aid infrastructure and support systems:
🏥 Hospitals and Clinics – Emergency departments with trained first responders
🏥 Public Health Centers – CPR and first aid training programs
🏥 School Programs – Basic life support and first aid incorporated into curricula
🏥 Workplace Safety Programs – Mandatory first aid training for employees in high-risk jobs
🏥 Public AED Deployment – Automated defibrillators in airports, subway stations, and malls
🏥 Volunteer First Responders – Red Cross, community volunteers trained in emergency care
Why Korea is Effective in First Aid Services:
✔️ High-quality training programs – Certification in CPR, BLS, and advanced first aid
✔️ Government-supported emergency services (119) – Rapid response nationwide
✔️ Public awareness campaigns – Promote first aid knowledge and AED use
✔️ Accessibility – Schools, workplaces, hospitals, and public spaces equipped for emergencies
✔️ Integration with emergency medical system – Seamless transfer from first aid to definitive care
Approximate Costs in Korea:
🔹 First aid training / CPR course → $30 – $100
🔹 Advanced life support courses → $200 – $400
🔹 AED purchase and installation → $1,000 – $2,500
🔹 Hospital emergency care after first aid → Variable, depending on injury or illness
Conclusion
First aid is an essential skill for everyone, bridging the gap between injury or illness onset and professional medical care.
It helps individuals:
✔️ Preserve life in emergencies
✔️ Reduce complications and long-term injury
✔️ Promote faster recovery
✔️ Empower communities with safety awareness
In Korea, first aid is widely accessible, highly regulated, and integrated with emergency services, offering:
✔️ Comprehensive training programs for all ages
✔️ Publicly available AEDs and first aid kits
✔️ Emergency response coordination with 119 services
✔️ Safe and effective initial care leading to better patient outcomes
👉 Key Message: First aid in Korea ensures timely, safe, and effective intervention in emergencies, saving lives and supporting overall public health.