What is Gallbladder Removal?
Gallbladder removal, medically known as cholecystectomy, is a surgical procedure to remove the gallbladder, a small organ located beneath the liver that stores bile. This procedure is commonly performed to treat gallstones, gallbladder inflammation, or other gallbladder disorders.
💡 Key Facts About Gallbladder Removal:
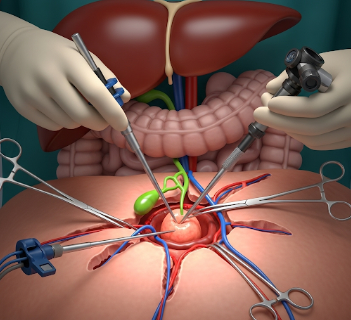
✔️ Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy – Minimally invasive surgery using small incisions and a camera (most common)
✔️ Open Cholecystectomy – Traditional surgery with a larger incision in the abdomen, usually reserved for complex cases
✔️ Purpose – Relieves pain, prevents complications like infection or bile duct blockage, and restores normal digestion
Gallbladder removal does not affect liver function or digestion significantly, although some patients may notice temporary changes in stool consistency or digestion of fatty foods.
In Korea, gallbladder removal is performed in advanced surgical centers, using state-of-the-art laparoscopic technology to ensure safety and fast recovery.
Why It’s Done
Gallbladder removal is recommended for conditions that cause pain, infection, or risk of serious complications.
✔️ Gallstones (Cholelithiasis) – Stones blocking bile flow cause pain, nausea, or jaundice
✔️ Gallbladder inflammation (Cholecystitis) – Leads to swelling, fever, and severe pain
✔️ Biliary dyskinesia – Poor gallbladder function causing digestive discomfort
✔️ Gallbladder polyps or cancer risk – Large polyps or suspicious growths may require removal
✔️ Prevention of complications – Avoids infection, pancreatitis, or bile duct obstruction
Clinical Benefits:
➡️ Relief from chronic pain – Eliminates recurrent gallbladder attacks
➡️ Prevention of severe complications – Reduces risk of infection and pancreatitis
➡️ Minimally invasive options – Laparoscopic surgery offers faster recovery and minimal scarring
➡️ High success rate – Over 95% of patients experience symptom resolution
In Korea, patients are evaluated with ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI, and surgery is recommended based on symptoms, gallstone size, and risk factors.
Alternatives
Before surgery, alternatives may be considered, especially for patients with mild symptoms or surgical risk:
⭐ Observation – Monitor asymptomatic gallstones without immediate intervention
⭐ Medication – Ursodeoxycholic acid may dissolve small cholesterol stones over time
⭐ Dietary modifications – Low-fat diet to reduce gallbladder irritation
⭐ Non-surgical procedures – Endoscopic or percutaneous treatments in selected cases
👉 Key Point: While alternatives may manage mild symptoms, surgery is the definitive treatment for symptomatic or complicated gallbladder disease.
Preparation
Proper preoperative preparation ensures safety and smooth recovery:
🔹 Medical evaluation – Blood tests, liver function tests, imaging studies (ultrasound, CT, MRCP)
🔹 Medication review – Adjust blood thinners, diabetes medications, or other chronic drugs
🔹 Fasting – Typically 6–8 hours before anesthesia
🔹 Informed consent – Understanding risks, benefits, and procedure details
🔹 Arrange post-surgery care – Assistance at home during initial recovery
⭐ Comfort measures – Loose clothing, support at home, and hydration
⭐ Mental preparation – Understanding procedure reduces anxiety
How It’s Done
Gallbladder removal can be performed using laparoscopic or open surgery:
- Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy
✔️ Small incisions (0.5–1 cm) made in the abdomen
✔️ Camera and instruments inserted to visualize and remove gallbladder
✔️ Bile ducts and arteries carefully clipped and dissected
✔️ Gallbladder removed through small incision; incisions closed with sutures or adhesive strips - Open Cholecystectomy
🔹 Larger incision in the upper right abdomen
🔹 Gallbladder carefully dissected and removed
🔹 Typically required for complex cases, previous abdominal surgery, or complications
Highlights:
✔️ Surgery duration – Usually 45–90 minutes
✔️ Anesthesia – General anesthesia
✔️ Hospital stay – Laparoscopic: 1–2 days; Open: 3–5 days
Recovery / Follow-up
Recovery after gallbladder removal varies by surgical method:
✔️ Immediate post-op care – Monitoring vital signs, pain management, and wound care
✔️ Pain management – Mild to moderate pain managed with analgesics
✔️ Diet – Gradually transition from liquids to normal diet; low-fat recommended initially
✔️ Activity – Light walking encouraged; avoid heavy lifting for 2–4 weeks
✔️ Follow-up appointments – 1–2 weeks post-surgery for wound check and suture removal
⭐ Long-term outcomes – Most patients resume normal activities within 1–2 weeks (laparoscopic)
⭐ Digestive adaptation – Some may experience loose stools or bloating initially; usually resolves within months
Complications / Risks
Gallbladder removal is generally safe, but potential risks include:
⚠️ Surgical site infection – Redness, swelling, or discharge
⚠️ Bleeding – Usually minor, may require intervention
⚠️ Bile duct injury – Rare but serious complication requiring further treatment
⚠️ Digestive issues – Temporary diarrhea, bloating, or fatty food intolerance
⚠️ Anesthesia-related complications – Allergic reactions, cardiovascular events, or respiratory issues
⚠️ Hernia at incision site – Rare, more common with open surgery
➡️ In Korea, experienced surgeons, advanced laparoscopic equipment, and sterile operating environments minimize risks significantly.
Treatment Options / Gallbladder Surgery in Korea
Korean hospitals offer state-of-the-art gallbladder removal services, including:
🏥 Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy – Standard procedure, minimally invasive
🏥 Open Cholecystectomy – For complex or high-risk cases
🏥 Robotic-assisted surgery – Available in specialized centers for precision
🏥 Pre- and post-operative counseling – Nutrition, recovery plan, and lifestyle advice
🏥 Follow-up care – Monitoring for complications, wound healing, and digestive adaptation
Why Korea is a Preferred Destination:
✔️ Expert hepatobiliary and general surgeons – Extensive experience in gallbladder surgery
✔️ Advanced laparoscopic and robotic equipment – Reduces pain, scarring, and recovery time
✔️ Comprehensive hospital care – Pre-op assessment, surgery, and post-op follow-up
✔️ Short hospital stay – Efficient, cost-effective treatment
✔️ High success rates – Excellent patient outcomes with low complication rates
Approximate Costs in Korea:
🔹 Laparoscopic Gallbladder Removal → $3,000 – $6,000
🔹 Open Gallbladder Surgery → $4,000 – $7,000
🔹 Hospital stay → $200 – $500 per day
🔹 Consultation and follow-up → $50 – $150
Conclusion
Gallbladder removal (cholecystectomy) is a safe, effective, and definitive treatment for gallbladder diseases, relieving pain, preventing complications, and improving quality of life.
It helps patients:
✔️ Avoid recurrent gallstone attacks
✔️ Prevent severe complications like infection, obstruction, or pancreatitis
✔️ Resume normal diet and activities
✔️ Achieve long-term relief and improved well-being
In Korea, patients benefit from:
✔️ Minimally invasive laparoscopic surgery with rapid recovery
✔️ Expert surgeons and comprehensive hospital support
✔️ Pre- and post-operative guidance for smooth recovery
✔️ Safe, cost-effective, and efficient treatment
👉 Key Message: Gallbladder removal in Korea provides modern, safe, and effective care, allowing patients to recover quickly and return to normal life with minimal discomfort and excellent outcomes.